Besides building and deploying your PowerServer project in the PowerBuilder IDE, you can also build and deploy your PowerServer project with a command-line tool (PBAutoBuild250.exe).
For convenience, you can directly export the configuration of an existing PowerServer project from the PowerBuilder IDE to a build JSON file. Therefore, you will need to prepare a proper environment first.
Step 1: Install the following software to set up the PowerBuilder development environment.
-
Windows 11 or 10
-
PowerBuilder IDE 2025
-
PowerBuilder Runtime 2025
-
PowerServer Toolkit 2025
Step 2: Follow Quick Start > Guide 1 to
-
create a PowerServer project for the Example Sales Demo;
-
build and deploy the PowerServer project (using the Build & Deploy PowerServer Project option in the PowerBuilder IDE) successfully; and
-
run the installable cloud app successfully.
Now let's export the PowerServer project settings of the Example Sales Demo to a JSON file.
You can export the current project or all projects from the workspace (or target).
To export the current project:
-
Open the workspace for the Example Sales App in the PowerBuilder IDE, and then double-click the PowerServer project object to open the object in the project painter.
-
When the project painter is opened, click the Export PowerServer Build File button (
 ) in the toolbar.
) in the toolbar.
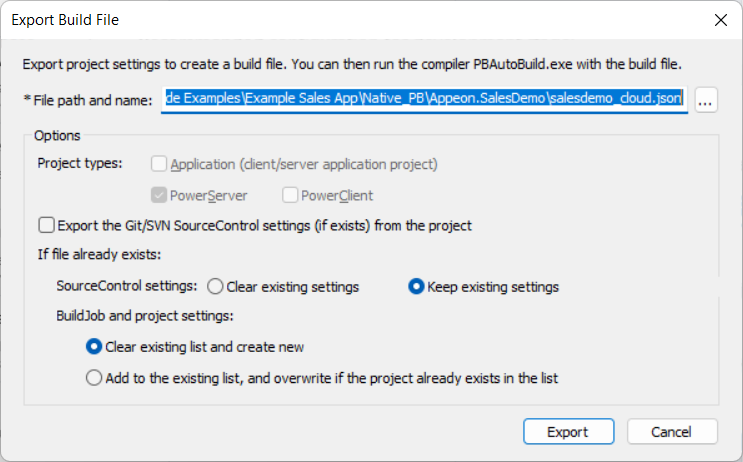
-
In the Export Build File dialog box, specify the settings, write down the path and filename to be exported, and then click Export.
For more information about the settings, refer to Build & deploy using commands.
The current project will be exported to the build file.
To export all of the projects from the workspace (or target):
-
Open the workspace for the Example Sales App in the PowerBuilder IDE, and then right click the workspace (or target) in the System Tree and select Export Build File.
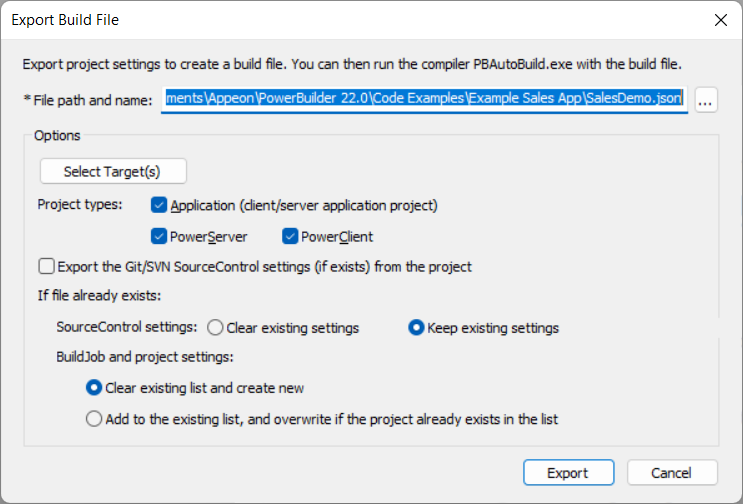
-
In the Export Build File dialog box, select which target(s) to be exported.
If the workspace contains multiple targets, then by default all targets will be exported to the same build file.
-
Select which project type(s) to be exported.
By default, all project types under the workspace (or target) will be exported to the build file.
-
Specify the settings, write down the path and filename to be exported, and then click Export.
The exported build file contains all the settings required for building and deploying the PBL files of the application and some additional settings.
|
Build file content |
Description |
|---|---|
"MetaInfo": {
"IDEVersion": "250",
"RuntimeVersion": "25.0.0.1311"
}, |
This section contains the version number of the PowerBuilder IDE and PowerBuilder Runtime currently in use. |
"BuildPlan": {
"SourceControl": {
"PreCommand": "",
"ClearSrcBeforeDownload": false,
"SVN": [
...
],
"Git": [
...
],
"VSS": [
...
],
"Merging": [
...
],
"PostCommand": ""
},
"BuildJob": {
"PreCommand": "",
"Projects": [
...
],
"PostCommand": ""
}
}, |
This section contains settings for source control and build jobs.
Both the "SourceControl" and "BuildJob" blocks contain a "PreCommand" key and a "PostCommand" key which allow you to specify commands that can be executed before and/or after that particular block is executed. See Executing additional commands for more examples. The commands in "PreCommand" and "PostCommand" can be executed in synchronous (default) or asynchronous mode, and the command window can be visible or invisible (default). For example, "PostCommand": "postcmd.bat /show /async" |
"Projects": {
"project1": {
...
},
"project2": {
...
},
"project3": {
...
},
...
} |
This section lists the project(s) that has been exported. Every single setting that can be found in the project painter can also be found here. You can modify the settings here when necessary. Besides the settings of the project painter, you could also configure the "UFAReport" key to enable/disable unsupported feature analysis for the PowerServer project (equivalent to the "During compilation, report unsupported PowerScript features for PowerServer deployment" option). NoteThe value of "namespace" should never be modified; the namespace is used internally to locate the PowerServer C# models and embedded SQLs. |
Settings in the build file are independent of each other; they run in sequence but do not rely on others or execution results, for example, if there is already source code in ws_objects, then you only need to set the Merging setting, and leave Git, SVN, and VSS empty as there is no need to download source code; or if there are PBLs in your Git server, then you only need to set the Git setting (to download PBLs) and leave the Merging setting empty. If you do not want a setting to run, just leave that setting with no values; or add "\\" in front of the setting name, for example, "\\Git" or "\\SourceControl", to skip the setting.
It is recommended that after you make a copy of the exported build file, you place it to the same location or a location near your PowerBuilder application target, so that you could manage the file path (especially the relative file path) easily.
Note: the relative path specified in the build file is relative to the build file.
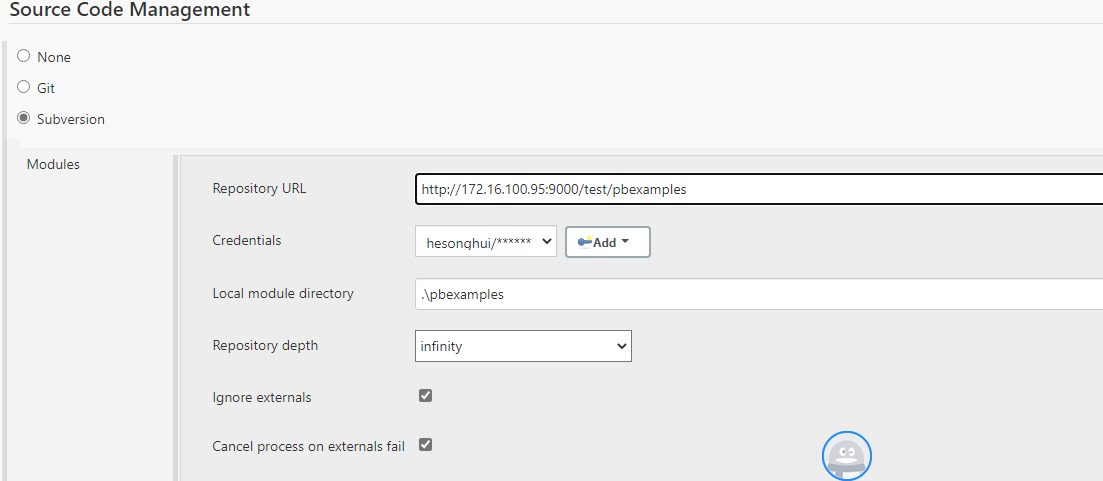
You can configure the exported build file to download source code from SVN, Git, or VSS before the build process starts.
Step 1: Open the build file in a text editor, locate the "BuildPlan" block and then configure the corresponding keys.
If the computer connects to Git or SVN through a proxy server, make sure to configure the proxy server in the "Proxy" part.
The following example shows how to download source code from Git:
"BuildPlan": {
"SourceControl": {
"PreCommand": "",
"ClearSrcBeforeDownload": false,
"SVN": [
{"SrcPath": "","User": "","Password": "","DestPath": "","Proxy": {"Ip": "","Port": 0,"Username": "","Password": ""}}
],
"Git": [
{"SrcPath": "https://github.com/Appeon/PowerBuilder-AutoBuild-Sales-SourceCode", "User": "tester@appeon.com", "Password": "YGRrYjc6OzU=", "DestPath": ".\\Build_Sales", "Branch": "", "Proxy": {"Ip": "","Port": 0,"Username": "","Password": ""}}
],
You can also download source code from multiple targets at one time:
"Git": [
{"SrcPath": "https://github.com/Appeon/PowerBuilder-AutoBuild-Sales-SourceCode", "User": "tester@appeon.com", "Password": "YGRrYjc6OzU=", "DestPath": ".\\Build_Sales", "Branch": "", "Proxy": {"Ip": "","Port": 0,"Username": "","Password": ""}},
{"SrcPath": "https://github.com/Appeon/PowerBuilder-AutoBuild-Examples-SourceCode", "User": "tester@appeon.com", "Password": "YGRrYjc6OzU=", "DestPath": ".\\Build_Examples", "Branch": "", "Proxy": {"Ip": "","Port": 0,"Username": "","Password": ""}}
],
The following example shows how to download source code from Team Foundation Server (TFS) or Azure DevOps Server:
IMPORTANT: To download source code from Team Foundation Server (TFS) or Azure DevOps Server, you will need to configure the "Git" section, and input your Personal Access Token (PAT) as the user name and password for connection.
"BuildPlan": {
"SourceControl": {
"PreCommand": "",
"ClearSrcBeforeDownload": false,
"SVN": [
{"SrcPath": "","User": "","Password": "","DestPath": "","Proxy": {"Ip": "","Port": 0,"Username": "","Password": ""}}
],
"Git": [
{"SrcPath": "https://402977329@dev.azure.com/402977329/kittytest/_git/kittytest","User": "402977329@qq.com","Password": "ZHFgcXVsZndtY2hicHJkZHxuMXlicXxufjF7OzVzOzB8ejpmcjthZz15eWB5aW0/bDV+eQ==","DestPath": "C:\\TFStest\\bug1853_1","Branch": "master","Proxy": {"Ip": "","Port": 0,"Username": "","Password": ""}}
],The following example shows how to download source code from VSS:
"BuildPlan": {
"SourceControl": {
"PreCommand": "",
"ClearSrcBeforeDownload": false,
"SVN": [
{"SrcPath": "","User": "","Password": "","DestPath": "","Proxy": {"Ip": "","Port": 0,"Username": "","Password": ""}}
],
"Git": [
{"SrcPath": "","User": "","Password": "","DestPath": "","Branch": "","Proxy": {"Ip": "","Port": 0,"Username": "","Password": ""}}
],
"VSS": [
{"SrcPath": "\\\\192.168.0.100\\Project_VSS\\\"$/Salesdemo/native_pb/appeon.salesdemo\", YYOAAAAA","User": "tester","Password": "","DestPath": ".\\Build_Sales"}
],
Notes:
1) Connecting to Git or SVN through a proxy server is supported, but connecting to VSS through a proxy server is not supported yet.
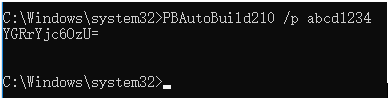
2) The password for VSS is not supported. The VSS login window will be displayed for you to input the password before downloading the source code. The password for SVN or Git must be an encrypted value which is generated from the original password by executing "PBAutoBuild250.exe /p", as shown below.
3) Getting an SVN/VSS branch is completely unsupported. Getting a Git branch can be supported by using the "Branch" setting.
Note
Merging source code into PBLs is required only for the workspace format.
If the source code downloaded from SVN, Git, or VSS is not the PBL file but objects in ws_objects, then you will need to merge the objects to the PBL file. Locate the "Merging" block in the build file and then configure it as below:
Setting "RefreshPbl" to true if you want to refresh the PBL files by deleting and then generating the PBL files again.
"Merging": [
{"Target": ".\\Build_Sales\\salesdemo.pbt", "LocalProjectPath": ".\\Build_Sales", "RefreshPbl": true}
],
You can also merge source code for multiple targets at one time:
"Merging": [
{"Target": ".\\Build_Sales\\salesdemo.pbt", "LocalProjectPath": ".\\Build_sales", "RefreshPbl": true},
{"Target": ".\\Build_Examples\\examples.pbt", "LocalProjectPath": ".\\Build_Examples", "RefreshPbl": true}
],
Merging will not only merge the source code but also upgrade the source code to the current version. However, it will not check or upgrade the PBD files used in the library list (you will need to replace the PBD files with the corresponding version).
At the same time, make sure to double check the target location is set correctly in the "Projects" block, for example,
"BuildJob": {
"PreCommand": "",
"Projects": [
{"Target": ".\\Build_Sales\\salesdemo.pbt", "Name": "ps_salesdemo"}
{"Target": ".\\Build_Examples\\examples.pbt", "Name": "pb_examplesdemo"}
],
"PostCommand": ""
}
When the PBAutoBuild250.exe command is executed later, it will first download the source code from the server and then merge the source code.
-
Create PBL file
-
Import objects into each PBL
-
Compile objects in the PBL.
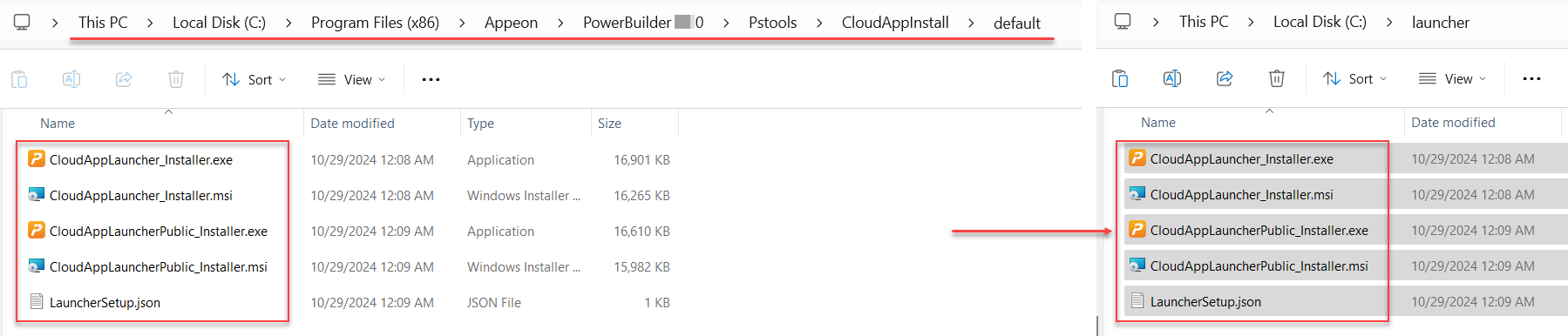
The command-line tool will not be able to upload the cloud app launcher if PowerBuilder IDE is NOT installed on the same machine. Therefore, you will need to copy the launcher from a machine with PowerBuilder IDE installed, and then modify the build file to point to that launcher, so that the tool can upload it to the server.
For example, copy the default launcher from C:\Program Files (x86)\Appeon\PowerBuilder [version]\Pstools\CloudAppInstall\default (or the customized launcher from %AppData%\CloudAppLauncher_Installer) to the current machine (suppose the location is C:\launcher).
And then modify the build file (the "CloudAppLauncherPath" setting) to point to the launcher location on the current machine (Use double backslashes (\\) instead of a single backslash (\) in the file path to avoid escape character issue):
"Advanced": {
"SelectTheLauncherToUpload": {
"CloudAppLauncher": true,
"CloudAppLauncherName": "Default",
"CloudAppLauncherPath": "C:\\launcher",
"RuntimeVersion": "",
"CloudAppLauncherMode": 0,
"RuntimeFiles": true
}
}The entire build & deploy process is made up of several steps, and additional commands can be executed before and/or after some particular steps such as the "SourceControl" and "BuildJob" steps.
Example 1: to add commands to remove a folder before downloading the source code.
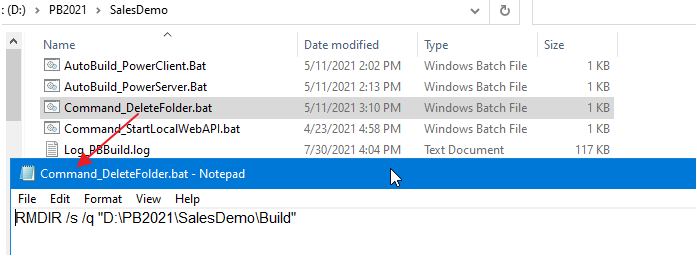
Step 1: Create a bat file which contains the following command, and save the bat file as Command_DeleteFolder.bat.
RMDIR /s /q "D:\PB2025\SalesDemo\Build"
Step 2: In the build file, locate the "BuildPlan" block and then the "PreCommand" setting; and add the file path and name of Command_DeleteFolder.bat.
"BuildPlan": {
"SourceControl": {
"PreCommand": "Command_DeleteFolder.bat",
"ClearSrcBeforeDownload": false,
"SVN": [
...
],
When the PBAutoBuild250.exe command is executed later, it will execute the commands in Command_DeleteFolder.bat before it downloads the source code.
Besides the "PreCommand" setting, there is also a "PostCommand" setting for the "SourceControl" and "BuildJob" steps, which allows you to execute commands after that particular step. See Example 2 and 3 for more details.
Example 2: to add commands to start the PowerServer Web APIs after building the PowerServer project in the PowerBuilder IDE.
Step 1: Create a bat file which contains the following command, and save the bat file as startwebapi.bat.
dotnet.exe run --no -build --project C:\Users\appeon\source\repos\PowerServer_salesdemo\ServerAPIs\ServerAPIs.csproj
Step 2: In the build file, locate the "BuildJob" block and then the "PostCommand" setting; and add the file path and name of startwebapi.bat.
"BuildJob": {
"PreCommand": "",
"Projects": [
...
],
"PostCommand": "startwebapi.bat /show /sync"
}
When the PBAutoBuild250.exe command is executed later, it will execute the commands in startwebapi.bat after it finishes building the PowerServer project.
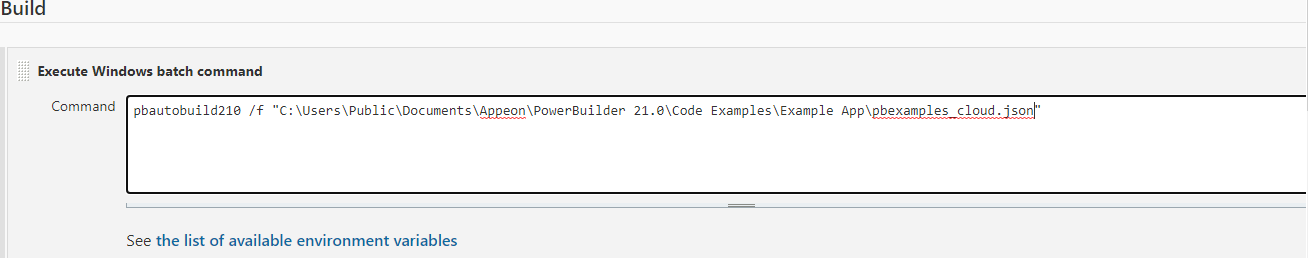
Example 3: to publish the PowerServer Web API after building the PowerServer project in the PowerBuilder IDE.
Step 1: Create a bat file which contains the following command, and save the bat file as publish.bat.
dotnet.exe publish C:\Users\appeon\source\repos\PowerServer_salesdemo\ServerAPIs\ServerAPIs.csproj -c release -o C:\Publish
Step 2: In the exported build file, locate the "BuildJob" block and then the "PostCommand" setting; and add the file path and name of publish.bat.
"BuildJob": {
"PreCommand": "",
"Projects": [
...
],
"PostCommand": "publish.bat /show /sync"
}
When the PBAutoBuild250.exe command is executed later, it will execute the commands in publish.bat after it finishes building the PowerServer project.
Note
The dotnet commands can also be integrated with Jenkins. See Task 2 for more details.
To build and deploy the PowerServer project using the command-line tool (instead of within PowerBuilder IDE), install the following software.
-
Windows 11 or 10, or Windows Server 2022, 2019, or 2016
-
PowerBuilder Utilities 2025
The command-line tool (PBAutoBuild250.exe) is included in PowerBuilder Utilities.
-
PowerBuilder Runtime 2025
The runtime files from the runtime packager are not sufficient for PBAutoBuild to run; you need to install PowerBuilder Runtime by following instructions in this section or install PowerBuilder Runtime in the silent mode by following instructions in this section.
-
PowerServer Toolkit 2025
The PBAutoBuild250.exe tool can automate the entire build and deploy process outside PowerBuilder (without needing any PowerBuilder license).
If the DB2, MySQL, Oracle, or Informix database connection is used, you will need to manually download the database driver from the NuGet website, by following instructions in the next section Preparing the database driver.
You need to manually prepare the database driver if the DB2, MySQL, Oracle, or Informix database connection is required.
Tips:
1) To unzip a NuGet package, you can change the file extension from .nupkg to .zip, and then unzip the file.
2) If you have PowerBuilder IDE installed on another machine, you can have PowerBuilder IDE download and install the driver automatically, and then directly copy the folder from there (without needing to manually download the driver). The section Download the database driver has detailed instructions.
3) If there is any inconsistency between the document and the product message regarding the minor version number of the driver, please follow the product message as the authoritative source.
4) Make sure that drivers are copied to the specified location, so that they can be automatically loaded by PBAutoBuild250.exe.
MySQL
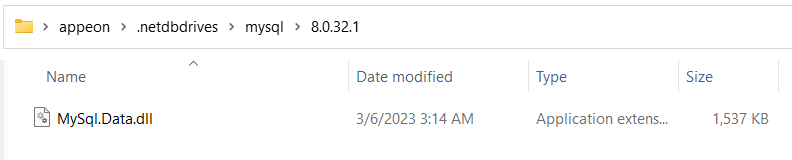
Step 1: Create the following directory under %USERPROFILE%: %USERPROFILE%\.netdbdrives\mysql\9.1.0.
Step 2: Copy the driver from the machine with PowerBuilder IDE installed (or manually download MySql.Data 9.1.0 and the license file).
Step 3: Unzip the file, and copy MySql.Data.dll from MySql.Data.9.1.0\lib\netstandard2.1\ to %USERPROFILE%\.netdbdrives\mysql\9.1.0.
Oracle
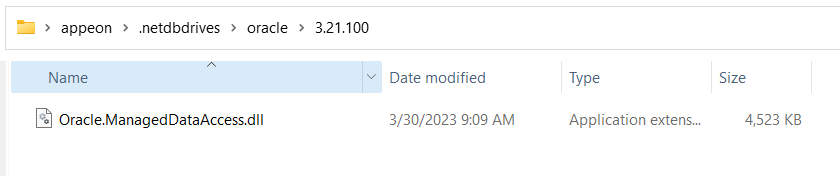
Step 1: Create the following directory under %USERPROFILE%: %USERPROFILE%\.netdbdrives\oracle\23.6.1.
Step 2: Copy the driver from the machine with PowerBuilder IDE installed (or manually download Oracle.ManagedDataAccess.Core 23.6.1 and the license file).
Step 3: Unzip the file, and copy Oracle.ManagedDataAccess.Core.dll from Oracle.ManagedDataAccess.Core.23.6.1\lib\netstandard2.1\ to %USERPROFILE%\.netdbdrives\oracle\23.6.1.
Informix / DB2
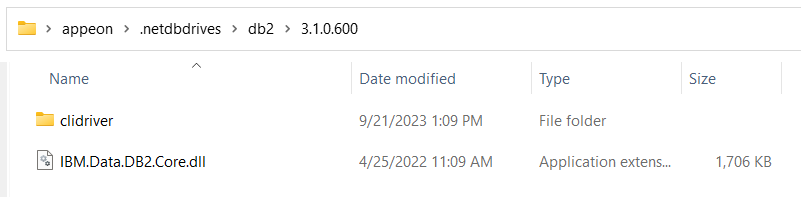
Step 1: Create the following directory under %USERPROFILE%:
For Informix: %USERPROFILE%\.netdbdrives\informix\8.0.0.300
For DB2: %USERPROFILE%\.netdbdrives\db2\8.0.0.300
Step 2: Copy the driver from the machine with PowerBuilder IDE installed (or manually download Net.IBM.Data.DB2 8.0.0.300 and the license file).
Step 3: Unzip the file.
Step 4: Copy the Net.IBM.Data.DB2.dll file from Net.IBM.Data.DB2.8.0.0.300\lib\netstandard2.1\ to %USERPROFILE%\.netdbdrives\informix\8.0.0.300 or %USERPROFILE%\.netdbdrives\db2\8.0.0.300.
Step 5: Copy the clidriver folder from Net.IBM.Data.DB2.8.0.0.300\buildTransitive to %USERPROFILE%\.netdbdrives\informix\8.0.0.300 or %USERPROFILE%\.netdbdrives\db2\8.0.0.300.
Step 1: Copy the exported build JSON file to the current machine and double check the file paths in the build file are appropriate to the current environment.
Step 2: Copy the application source code (including PBT/PBPROJ, PBL, PBR, images, INI etc.) to the current machine, or configure the build file to download source code from the source control server.
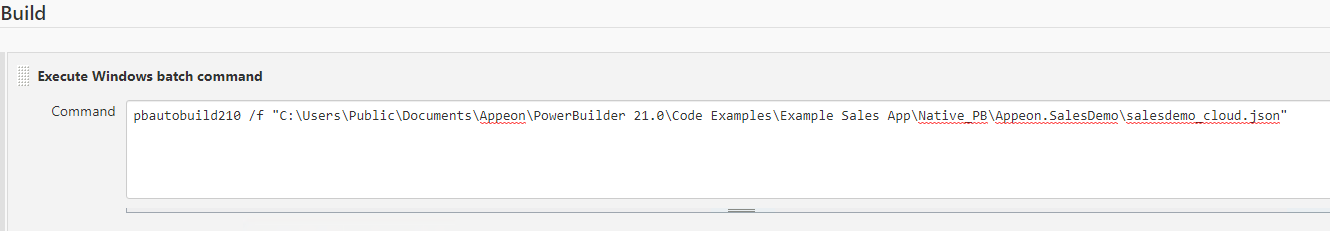
Step 3: In the command-line window, execute the PBAutoBuild250.exe file and the build file. For example,
PBAutoBuild250.exe /f "D:\PB2025\SalesDemo\ps_salesdemo.json" /l Log_PSBuild.log /le Log_PSError.log /lu Log_PSUnsupport.log
The PBAutoBuild250.exe file can be run with parameters. For a complete list of supported parameters, refer to PBAutoBuild supported parameters.
Step 4: Carefully check the information in the command-line window to make sure the build and deploy process is successful.
The build file and commands used in this guide can be downloaded from https://github.com/Appeon/PowerBuilder-AutoBuild-Sales-Example. After you download these files to D:\PB2025\SalesDemo\, you can follow the instructions in the readme file.
After executing the PBAutoBuild250.exe file and the build file,
you can check if the execution is successful via the Windows
command errorlevel:
-
errorlevel = 0 indicates the process was successful.
-
errorlevel = 1 indicates the process encountered an error.
You can write scripts as below to check the execution result:
Echo off
PBAutoBuild250.exe /f "D:\PB2025\SalesDemo\ps_salesdemo.json" /l Log_PSBuild.log /le Log_PSError.log /lu Log_PSUnsupport.log
If %ERRORLEVEL% == 0 (
echo Run PBAutoBuild successfully.
) Else (
echo Failed to run PBAutoBuild, Errorlevel is %ERRORLEVEL%.
)The PBAutoBuild250 command can integrate with Jenkins to automate the build and deployment process for PowerServer projects. Refer to the Jenkins user documentations for how to use Jenkins.
Following gives a few examples on how to integrate the PBAutoBuild250 and dotnet commands with Jenkins.
Example 1: to execute the PBAutoBuild250 command and the build file.
Example 2: to download source code from SVN, Git, or VSS, and then execute the PBAutoBuild250 command and the build file.
Double check that the PBT location is the same one in all required areas.
Example 3: to publish or run the PowerServer Web APIs
You can integrate dotnet commands with Jenkins. After you install the .NET SDK Support plugin for Jenkins, the dotnet commands (for example, dotnet publish, dotnet run etc.) are available as shown below. Refer to https://www.jenkins.io/doc/pipeline/steps/dotnet-sdk/ for more details.