The PowerServer C# solution is generated when you select the
Build & Deploy PowerServer Project
button ( ) in the toolbar. After the solution is generated,
you can click the Open C# Solution in
SnapDevelop button (
) in the toolbar. After the solution is generated,
you can click the Open C# Solution in
SnapDevelop button ( ) in the toolbar to launch the PowerServer C#
solution in SnapDevelop. Or go to the location where the solution is
generated; and double click PowerServer_[appname].sln to launch the solution
in SnapDevelop or other C# editor such as Visual Studio.
) in the toolbar to launch the PowerServer C#
solution in SnapDevelop. Or go to the location where the solution is
generated; and double click PowerServer_[appname].sln to launch the solution
in SnapDevelop or other C# editor such as Visual Studio.
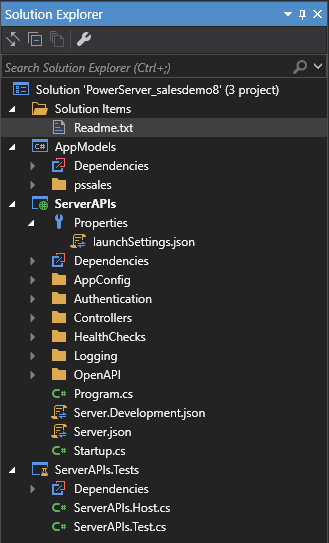
The PowerServer C# solution is an ASP.NET Core solution which contains three projects:
-
The AppModels project contains the C# models (converted from the PowerBuilder DataWindows) and the embedded SQLs (ESQL) from the PowerBuilder application.
-
The ServerAPIs project contains the PowerServer Web APIs which is RESTFul APIs for handling the database connections, data processing, PowerServer license activation, and advanced features such as file server etc. You run the ServerAPIs project to start the PowerServer Web APIs. For detailed steps, refer to Run the PowerServer Web APIs.
-
The ServerAPIs.Tests project contains a number of test cases which can check if the PowerServer Web APIs is running correctly after the ServerAPIs project is modified. See Running the ServerAPIs.Tests project for more details.
Among these three projects, only the ServerAPIs project contains a number of configurable files and controllers. The following highlights the important files and settings only. For complete descriptions, refer to the readme.txt file under Solution Items.
-
Properties\launchSettings.json: This file contains the environment settings for running the PowerServer Web APIs in the local development environment, for example, the commandName key specifies the web server to launch (the value "Project" indicates that the Kestrel server will be launched), and the applicationURL key specifies the host name and port number for the server. For the description of the settings in this file, See https://docs.microsoft.com/aspnet/core/fundamentals/environments?#development-and-launchsettingsjson.
-
AppConfig
-
AppConfig.json: This file specifies the environment (such as the DB connection profile) to be used when starting PowerServer Web APIs.
"POWERSERVER_ENVIRONMENTTYPE": Specifies the DB connection profile used for starting PowerServer Web APIs. By default, the DB connection profile that is currently selected in the project painter > Database page is set in this file. Refer to Create the DB connection profile for more information.
"ConnectionStrings": Specifies the connection string of the database. You could store the database connection (including the cache, application settings, and transaction-to-cache mappings) in this database instead of in Applications.json or Applications.[DBConnectionProfile].json, so that you could modify, add, or delete the database connection through APIs. For more, refer to Managing database connections using APIs.
"POWERSERVER_ENVIRONMENTTYPE": "Default", "ConnectionStrings": { "AppConfig": "<appconfig connection string>" } -
AppConfig.xml: This file sets the environment (mainly the DB connection profile) to be used when publishing the PowerServer Web APIs.
The default value is empty, meaning that all of the configured DB connection profiles will be deployed.
<POWERSERVER_ENVIRONMENTTYPE></POWERSERVER_ENVIRONMENTTYPE>
-
Applications.json or Applications.[DBConnectionProfile].json: This file contains the basic information of the deployed applications and the database connection cache settings.
For each DB connection profile configured in the Database page, an Applications.[DBConnectionProfile].json file is created. Applications.json is for the "Default" DB connection profile.
-
"Applications": This block includes a list of the deployed applications and the mappings of transactions and connection caches, timeout values for transaction, session, and request, and run mode (0-normal mode, 1-test mode) of each deployed application.
Take the following settings for example, in the "salesdemo_cloud" application, the "sqlca" transaction object is mapped to the "sales" database cache. Refer to Managing transaction-to-cache mappings in the PowerServer solution for more information.
To understand and set appropriate timeout values for "Transaction", "Session" and "Request", refer to Configure timeout settings.
You can run the application in test mode ("RunMode": 1) if you want to perform load-testing for the application. For more, refer to Tutorial: Load testing installable cloud apps.
"Applications": { "salesdemo_cloud": { "CloudTransactions": { "sqlca": { "CacheName": "sales" } }, "Transaction": { "Timeout": 120, "TransactionException": true }, "Session": { "Timeout": 3600 }, "Request": { "Timeout": 3600 }, "RunMode": 0 } }, -
"Connections": This block includes a list of the cache groups and caches.
Take the following settings for example, the "Default" cache group contains the "sales" cache, and the connection settings vary according to the database type (refer to your DBMS documentation for more information).
"Connections": { "Default": { "sales": { "ConnectionType": "Odbc", ...... } } }"ConnectionType": The connection type. For SQL Anywhere and ASE databases, only ODBC connection type is supported; for the other databases, the native connection type is supported.
-
0: SqlServer
-
2: Oracle
-
3: MySql
-
5: PostGreSql
-
6: Odbc
-
7: Informix
"OdbcName": (For ODBC connections) The ODBC data source name.
"OdbcDriver": (For ODBC connections) The ODBC driver.
"Database": (For native connections) The database name.
"Host": (For native connections) The host name or IP address of the database server.
"Port": (For native connections) The port number of the database server.
"UserID": The database login user name.
"Password": The database login password. The password can be an encrypted value (encrypted by the CustomizeDeploy.dll tool) or a plain-text string.
"EnablePooling": Whether to enable the pooling feature.
"MinPoolSize": The minimum number of connections that are allowed in the pool. Refer to your DBMS documentation for more information.
"MaxPoolSize": The maximum number of connections that are allowed in the pool. Refer to your DBMS documentation for more information.
"ConnectionLifetime": When a connection is returned to the pool, its creation time is compared with the current time, and the connection is destroyed if that time span (in seconds) exceeds the value specified by Connection Lifetime. This is useful in clustered configurations to force load balancing between a running server and a server just brought online. Refer to your DBMS documentation for more information.
"ConnectionTimeout": The length of time (in seconds) to wait for a connection to the server before terminating the attempt and generating an error. Refer to your DBMS documentation for more information.
"CommandTimeout": The wait time before terminating the attempt to execute a command and throwing an error. Refer to Configure timeout settings.
"SecurityOptions": The security options for the database connection, such as Authentication, Encrypt, Integrated Security, Trust Server Certificate, Persist Security Info, User ID, Password etc. The security options vary according to the database type. You can view all available options in the project painter > Database page > Basic tab > More button > Advanced dialog > Security category.
"SecurityOptions": "encrypt=True;trust server certificate=True"
"OtherOptions": Any database connection option that is available in the project painter > Database page > Basic tab > More button > Advanced dialog. However, it should not include those listed separately as standalone settings (such as Database, UserID, Password, EnablePooling, CommandTimeout etc.). The settings in "OtherOptions" have higher priority (and will overwrite the standalone settings). And "OtherOptions" must not include the settings in the Advanced dialog > Other category, such as DelimitIdentifier, Is Nullable Type, and Outer Join Syntax; these settings are used for DataWindow-to-model conversions only, not for database connections; if these settings are included in "OtherOptions", database connection errors will occur.
"OtherOptions": "Connect Retry Count=1; Connect Retry Interval=10"
"DynamicConnection": Whether the app connects to the database based on the user credentials provided at runtime. When it is set to true, the application will either use the LogID and LogPass property values of the Transaction object or the UID and PWD values in the ConnectString DBParm parameter to log in to the database server (instead of using the values in the User name and Password fields of the cache). For more, refer to Using LogID and LogPass properties.
Following is a cache for SQL Anywhere:
"sales": { "ConnectionType": "Odbc", "OdbcName": "PB Demo DB V2022", "OdbcDriver": "SqlAnywhere", "UserID": "dba", "Password": "eyJQYXlsb2FkIj******", "CommandTimeout": 30, "SecurityOptions": null, "OtherOptions": null, "DynamicConnection": false },Following is a cache for PostgreSQL:
"sales_postgresql": { "ConnectionType": "PostgreSql", "Database": "PBDemo", "Host": "127.0.0.1", "Port": 5432, "UserID": "postgres", "Password": "eyJQYXlsb2FkIj******", "EnablePooling": true, "MinPoolSize": 0, "MaxPoolSize": 100, "ConnectionLifetime": 0, "ConnectionTimeout": 15, "CommandTimeout": 30, "SecurityOptions": null, "OtherOptions": null, "DynamicConnection": false }, -
-
-
-
Authentication: This folder contains the template and built-in server for the selected authentication type. For more information, refer to Tutorial: Authenticating your apps.
-
Controllers
-
ApplicationController.cs: This file provides APIs for dynamically adding, modifying or removing the application settings and transaction mappings.
-
ConnectionController.cs: This file provides APIs for dynamically adding, modifying or removing the cache or cache group.
-
LicenseController.cs: This file provides APIs for dynamically accessing the license information.
-
SessionController.cs: This file provides APIs for getting all user sessions or killing a particular user session.
-
StatisticsController.cs: This file provides APIs for getting statistics of the request and transaction.
-
TransactionController.cs: This file provides APIs for getting all transactions or rolling back a particular transaction.
For documentation of these APIs, refer to Use PowerServer Management APIs.
-
-
HealthChecks: For more information, refer to Check the status of Web APIs and the readme.txt file under Solution Items.
-
Logging: For more information, refer to Configure log settings.
-
OpenAPI: The OpenAPI Specification for exposing the API documentation in Swagger UI.
-
Server.json or Server.Development.json: This file contains settings related with the server. As you can use multiple environments in ASP.NET Core (read more), there can be multiple configuration files, for example, Server.json will take effect in the production environment (for example, when Web APIs are published and running in IIS, docker etc.), while Server.Development.json will take effect in the development environment (for example, when Web APIs is running from the SnapDevelop IDE or the PowerBuilder IDE).
-
"PathBase": Specifies the sub-folder of the Web site where PowerServer Web APIs is deployed, for example, "/vpath1", or null if no sub-folder is used.
-
"AllowedHosts": Specifies the host names to bind with PowerServer. See Host filtering for more.
-
"PowerServer": This block specifies the settings for PowerServer.
-
"LicenseKey" & "LicenseCode": PowerServer license information. Refer to Importing the PowerServer license for more information.
-
"EncryptedSensitiveData": Sensitive data refers to the database login password which is used to create the database connection cache in AppConfig\Applications.json. If the password is an encrypted value (encrypted by the CustomizeDeploy.dll tool), this setting should be set to True; if the password is not encrypted (still a plain-text string), this setting should be set to False so that PowerServer will encrypt the password for you and store the encrypted value to the database. If this setting is set to True and you input a plain-text password, the plain-text password will be directly stored to the database.
-
"AppModelsAssemblyNames": AppModels assembly name.
-
"ProxyOptions": The IP address and login credentials of the proxy server. If the Web API host server connects to Internet through a proxy server, you will need to configure the proxy server settings here. The password for the proxy server must be an encrypted value (encrypted by the CustomizeDeploy.dll tool).
-
"EmailOptions": This block must be configured first if you want to get notifications for license expiration. The settings include the SMTP server settings, sender email settings, and recipients. Refer to Configuring the email settings for more information.
-
"StatisticsOptions": This block determines which type of transaction statistics will be generated and cached in the memory. Some settings are disabled by default to lower memory usages. You can also take advantage of the StatisticsController APIs in PowerServer to get the statistics.
"PathBase": null, "AllowedHosts": "*", "PowerServer": { "LicenseKey": "DSCE-IHFG-CHEI-51H3-G0BE", "LicenseCode": "eyJQYXlsb2FkIjoiVT*****", "EncryptedSensitiveData": false, "AppModelsAssemblyNames": [ "AppModels.dll" ], "ProxyOptions": { ... }, "EmailOptions": { ... }, "StatisticsOptions": { ... }, -
-
For files that are not mentioned here, refer to the readme.txt file under Solution Items for more information.