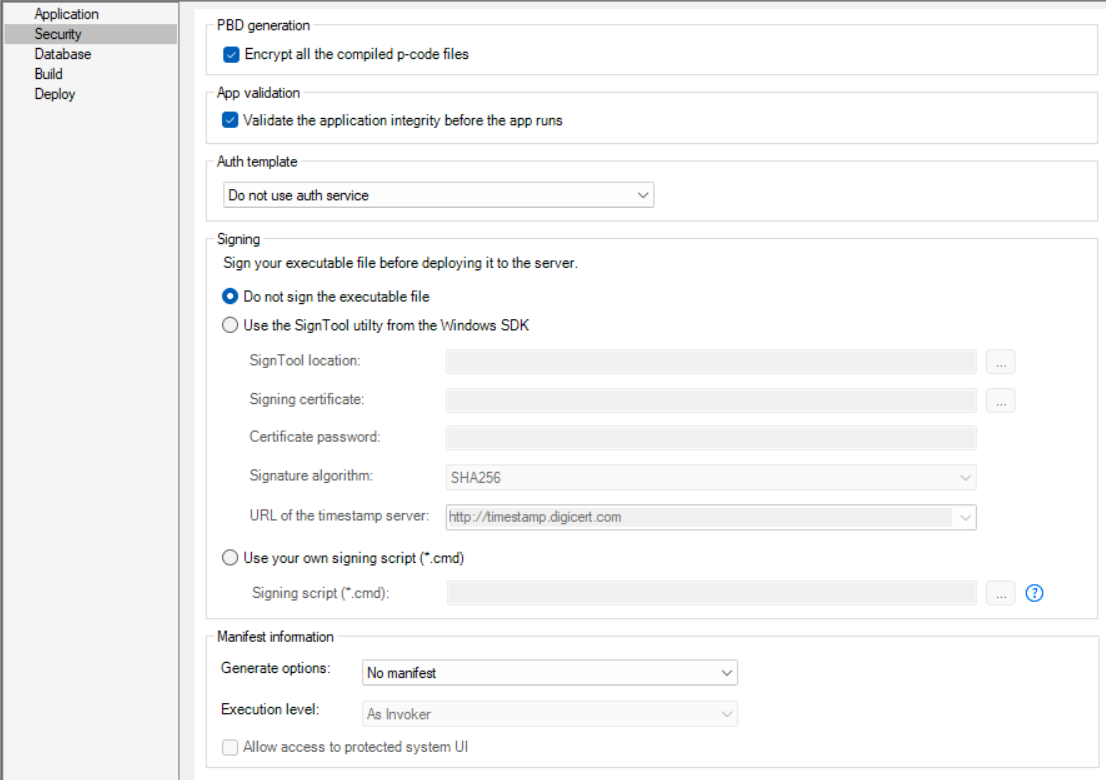
The Security page has the following settings:
|
Option or option group |
What you specify |
|---|---|
|
Encrypt all the compiled p-code files |
Select whether to encrypt the object files when compiled from the PowerBuilder dynamic libraries. |
|
Validate the application integrity before the app runs |
Specify whether to validate the hash of every object file before they are loaded, so that files changed illegally will not be run. |
|
Auth Template |
Specify the authentication template for PowerServer Web APIs. For more information, refer to Select an authentication template. |
|
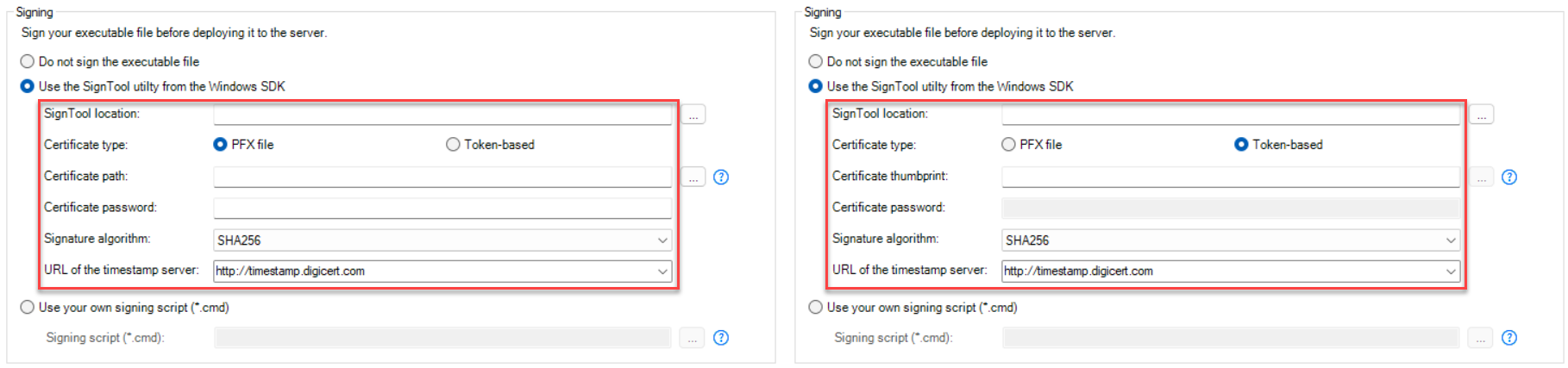
Select whether to digitally sign the application executable file (appname.exe). You can sign the file using a PFX file or a token. (To sign with an HSM (Hardware Security Module), you can only use the "Use your own signing script" option.) To use the "Use the SignTool utility from the Windows SDK" option to sign the application executable file:
To use the "Use your own signing script" option, you should place the signing scripts in a file (with file extension as .cmd) and then select the file under the "Use your own signing script" option. To sign with an HSM (Hardware Security Module), you can only use the "Use your own signing script" option. Take the PFX file for example,
Take the token for example,
To avoid repeatedly entering the UKey password (for instance the screen is locked or the system is restarted), you can use the "Use your own signing script" option and specify the token password in the signing commands, for example: "D:\test_newsign\signcode.exe" sign /fd SHA256 /a /sha1 "13731a37233bbd83eeb13e95c7898d1d76a2256c" /tr http://timestamp.digicert.com /td SHA256 -f "D:\test_newsign\cersign.cer" /csp "eToken Base Cryptographic Provider" /K "[{{a*****}}]=p11#f408f337487afa2d" "echarts_cloud.exe"
Note: 1) When writing scripts in the .cmd file, please follow the rules of Windows commands. If there are any exceptions or errors in the logs after configuring the "Use your own signing script" option, try running the scripts in the Windows Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell to identify the issue. 2) For .cmd files without dynamic parameters, both the directory name and the .cmd file name can contain spaces. However, for .cmd files with dynamic parameters, the directory path should not contain spaces, while the .cmd file name itself can contain spaces. 3) When entering the file path of the .cmd file in the "Use your own signing script" text box, follow the standard rules for accessing file paths in Windows. If the file name or path contains spaces, use double quotes to avoid escape errors. It is recommended to use absolute paths for the .cmd file and the parameters. After the executable file is generated and before it is deployed to the server, PowerBuilder will sign the executable file using your own signing scripts or using the SignTool settings you specified. Make sure the PowerBuilder user has the appropriate rights to access the time stamp server and sign files. |
|
|
Manifest Information |
Select whether to generate a manifest file (either external or embedded) and to set the execution level of the application. For further information, see Attaching or embedding manifest files in PowerBuilder User Guide. |