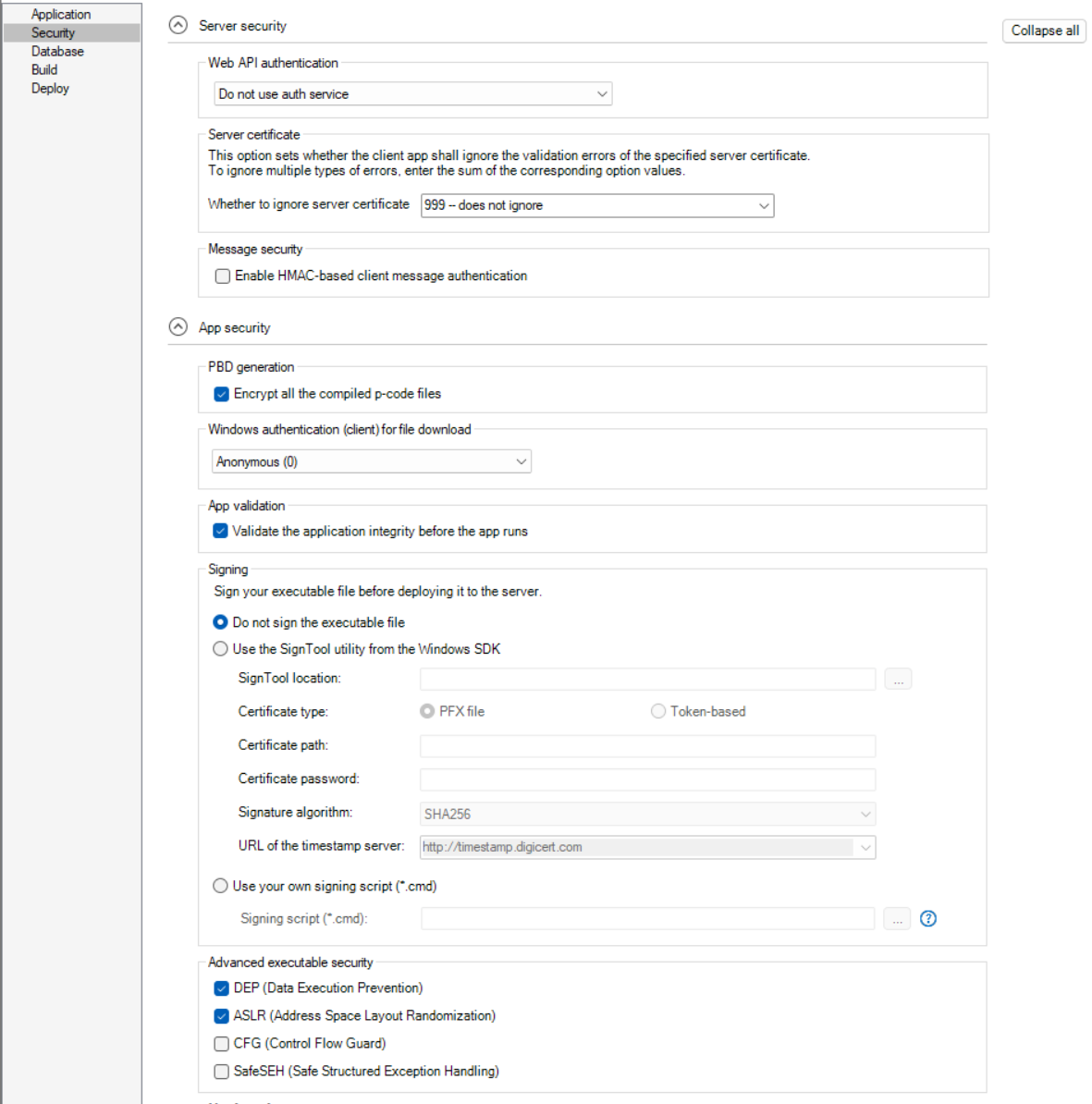
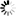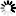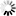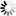The Security page has the following settings:
|
Option or option group |
What you specify |
|---|---|
|
Web API authentication |
Specify the authentication option to be used when accessing the PowerServer Web APIs. For more information, refer to Select an authentication option. |
|
Whether to ignore server certificate |
Select or input a value or a sum of values, if you want the installable cloud app to ignore certain type(s) of server certificate error when sending a request. For more information, refer to Ignore server certificate errors. |
|
Enable HMAC-based client message authentication |
Specify whether to use the HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) algorithm to safeguard the request data from tampering. (Note: the response data is not authenticated using HMAC.) When the client sends a request, it generates a unique authentication code based on the request data; the server receives the request and verifies the authentication code to ensure the data has not been altered. This option prevents unauthorized modifications and provides extra protection through encryption and authentication, keeping data secure and unchanged. Do not select this option if you want to perform load-testing for the application, otherwise you will get this error when replaying the test script: "Session fails to respond (Invalid session)". |
|
Encrypt all the compiled p-code files |
Select whether to encrypt the object files when compiled from the PowerBuilder dynamic libraries. |
|
Windows authentication (client) for file download |
Select the Windows authentication to be used when the client downloads the application files (for example, via the Cloud App Launcher). Three options are available:
The selected option will be stored in
|
|
Validate the application integrity before the app runs |
Specify whether to validate the hash of every object file before they are loaded, so that files changed illegally will not be run. |
|
Select whether to digitally sign the application executable file (appname.exe). For step-by-step instructions, refer to Code Signing > Using PowerBuilder code signing options. To use the "Use the SignTool utility from the Windows SDK" option:
To use the "Use your own signing script" option, you should place the signing scripts in a .cmd file and then select the file under the "Use your own signing script" option. You can take advantage of this option and dynamic parameters to make your script reusable. |
|
|
Advanced executable security |
Select the desired security flags for the application executable file (appname.exe). PowerBuilder Runtime files will support these security flags in the future release. These flags allow PowerBuilder applications to leverage modern Windows executable security features.
|
|
Third-party DLL loading scope |
Select the Strict mode option and then input the path of the third-party DLLs to limit the DLL search scope to the defined paths, preventing unauthorized or unexpected DLLs from being loaded. You should input only the path of the third-party DLLs. There is no need to input the runtime path, because the runtime DLLs will be automatically loaded from the directory according to the runtime version, for example, %localappdata%\PBApps\Applications\Runtime\25.0.0.3599. Select the Enable DLL signature verification option, so that the application will verify the digital signature of DLLs at startup. Note: only Appeon-signed DLLs will be verified by PowerBuilder. For more information, refer to DLL secure loading. |
|
Manifest Information |
Select whether to generate a manifest file (either external or embedded) and to set the execution level of the application. For further information, see Attaching or embedding manifest files in PowerBuilder User Guide. |