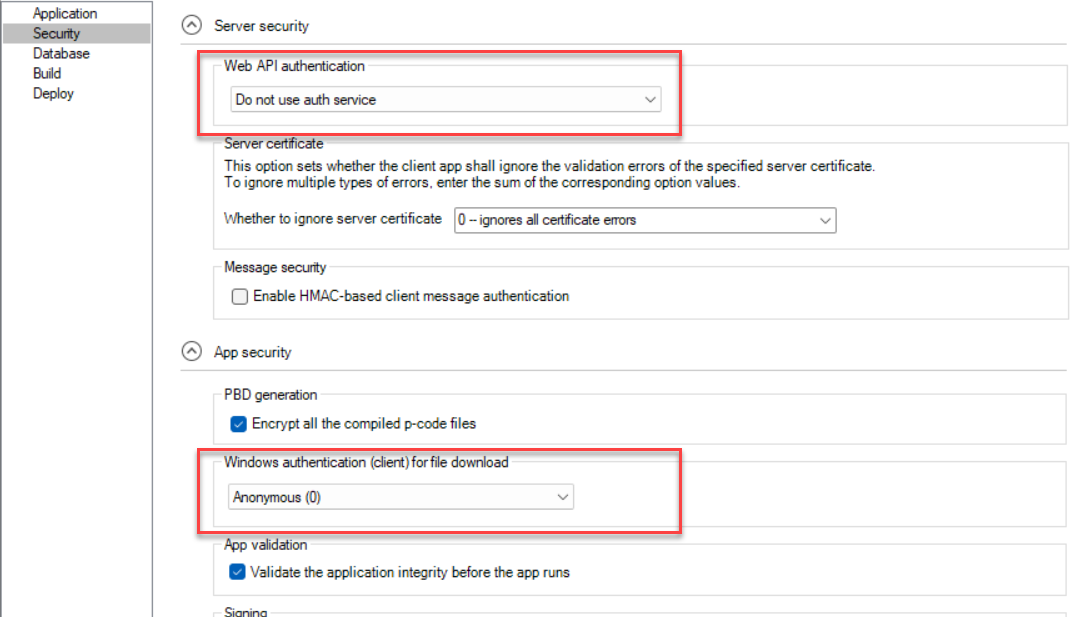
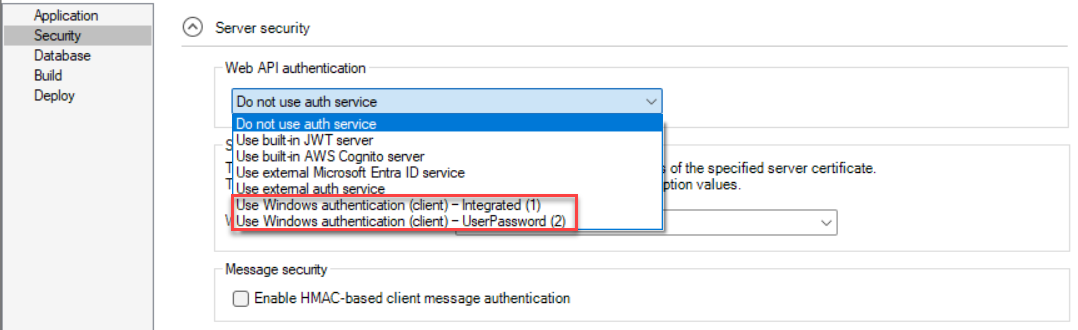
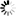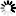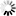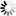From the Web API authentication list, choose the authentication method to be used when the client accesses the PowerServer Web APIs.
You can also choose to use the Windows-based authentication, either in the IDE or via scripts (scripts will override IDE settings).
-
Do not use auth service: Equivalent to anonymous access, users can access without providing credentials. This option is generally used for testing or for resources intended to be publicly accessible. It provides no security protection and should not be used in production unless required.
-
Use Windows authentication (client) - Integrated (1) - Automatically uses the client's Windows login for authentication. If authentication fails, a Windows security dialog may appear.
-
Use Windows authentication (client) - UserPassword (2) - Prompts the user to manually enter Windows credentials in a login dialog. Users can choose to save their credentials by selecting "Remember me" in the login dialog for future use (and can remove the cached credentials through the Windows Credential Manager later).
The selected Windows authentication mode will be stored in
appconfig.json on the server. You can use the
CloudAppGet
and CloudAppSet
functions to get and change the Windows authentication mode at
runtime.
From the Windows authentication (client) for file download list, choose the Windows-based authentication to be used when the client downloads the application files (via the cloud app launcher).
-
Anonymous (0) - No authentication is required for file downloads. Users can download files without providing credentials.
-
Integrated (1) - The client automatically uses the current Windows login for authentication. If authentication fails, a Windows Security dialog may appear.
-
UserPassword (2) - The user is prompted to enter Windows credentials in a login dialog. Users can choose to save their credentials for future use (cached in Windows Credential Manager).
The selected mode will be stored in apprun.json
on the server (remember to include apprun.json when
deploying the app) and in pbapp.ini on the client.
(Unlike Web APIs, authentication mode for file download cannot be
changed via scripts at runtime.)
Windows considers each type of access — such as opening a website, downloading application files, or calling a Web API — as an independent resource. For security, Windows performs a separate authentication check for each resource. That means even though all these actions belong to the same application, Windows still verifies credentials separately, ensuring that access to one resource does not automatically grant access to another.
Because of this, users may see more than one login prompt, in the following scenarios within PowerServer (PowerClient is similar with scenario 1 and 2):
-
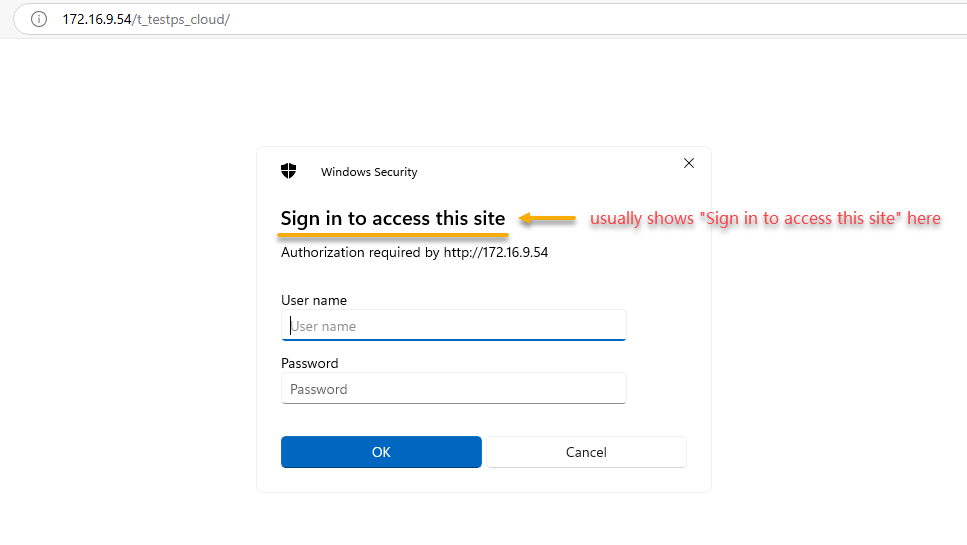
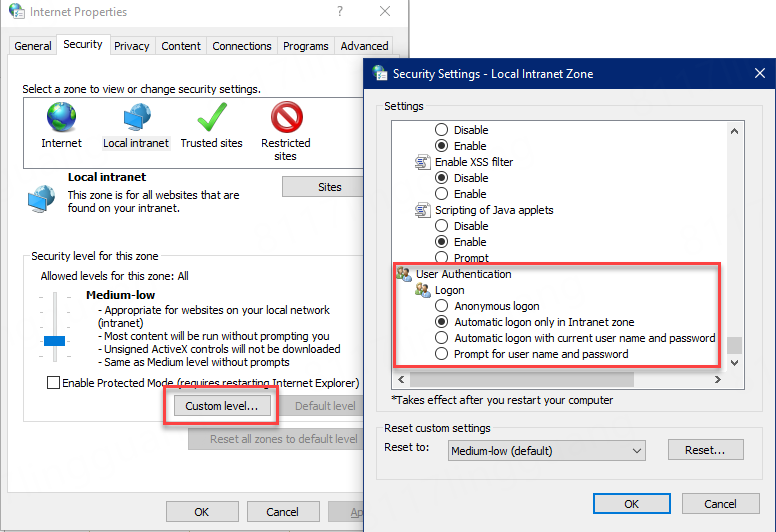
Scenario 1: Accessing the Website
When opening the Web Portal, IIS or a proxy may ask for Windows login (often shown as "Sign in to access this site"). This is standard Windows behavior.
-
When it appears: If IIS has enabled Windows authentication and the application is accessed from a web browser.
-
How to avoid it: This prompt is NOT related to the PowerServer project settings. You can change the browser settings to avoid this prompt, or launch the application from a desktop shortcut (no prompt).
-
-
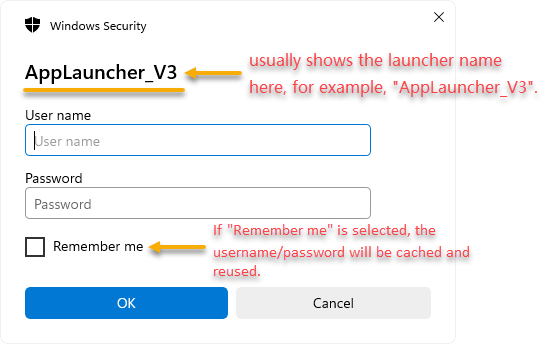
Scenario 2: Downloading the app via launcher
When the Cloud App Launcher downloads app files, it may ask for login. The dialog usually shows the launcher name (for example, "AppLauncher_V3").
-
When it appears: If IIS has enabled Windows authentication and the PowerServer app security is set to Windows authentication (User password).
-
How to avoid it: Change the PowerServer app security to Windows authentication (Integrated).
-
-
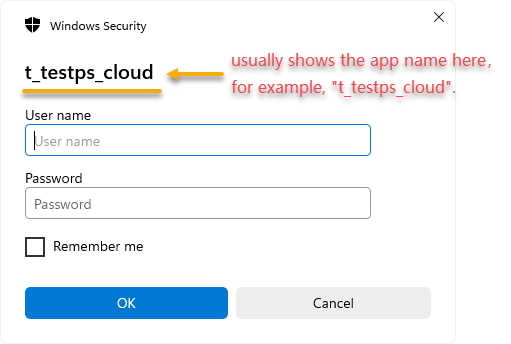
Scenario 3: Calling Web APIs from the app
When the app calls the Web API, another login may appear. The dialog usually shows the app name (for example, "cloudapp1").
-
When it appears: If IIS has enabled Windows authentication and the PowerServer Web API authentication is set to Windows authentication (User password).
-
How to avoid it: Change the PowerServer Web API authentication to Windows authentication (Integrated). Alternatively, if the user selected "Remember me" (not selected by default), the credentials will be cached and automatically reused on the client. Users can later remove these cached credentials through the Windows Credential Manager.
-
These prompts are not duplicates—they are Windows' way of protecting different resources separately. If your environment uses Kerberos or SSO, Windows reuses the credentials silently, so users normally only log in once. If NTLM or Basic authentication is used, prompts may appear more than one time.
If you use IIS to host PowerServer Web APIs and/or application files, configure it properly to enable Windows Authentication.
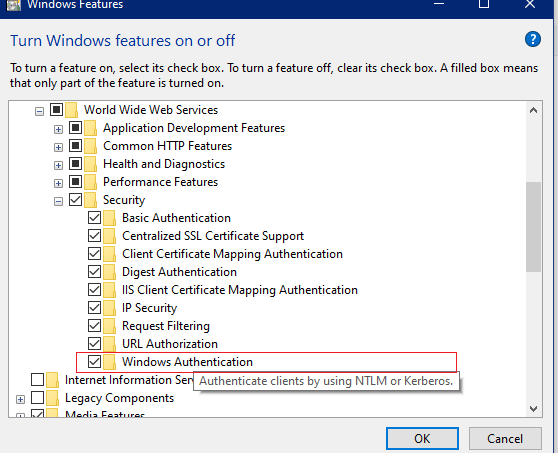
Step 1: Enable IIS Windows Authentication Feature
-
Open Server Manager on the Windows server.
-
Go to Add Roles and Features.
-
Under Server Roles, make sure Web Server (IIS) is installed.
-
In Role Services, enable Windows Authentication.
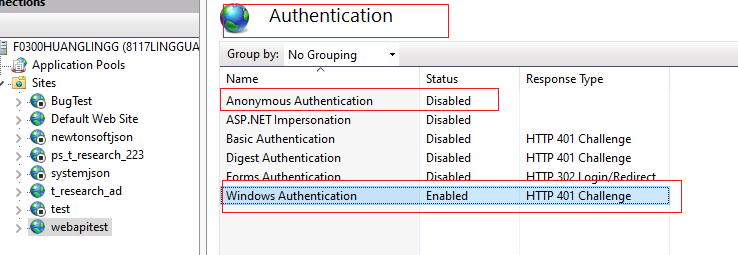
Step 2: Configure IIS Authentication for the Application
-
Open the IIS Manager and navigate to the application site.
-
Select Authentication under the IIS section.
-
Enable Windows Authentication.
-
Disable Anonymous Authentication if you want to force Windows login.
Step 3: Configure Authentication in PowerServer Project
After IIS has been set up, configure the authentication mode inside the PowerServer project:
-
In the project painter, go to the Security page.
-
For Web APIs, select the authentication mode under Web API authentication.
-
For app file downloads, select the authentication mode under Windows authentication (client) for file download.