A server profile is a set of parameters for PowerServer Toolkit to connect to, and deploy applications to, a particular PowerServer or Web server. Creating and using server profiles is the easiest way to manage your application deployments because you can:
-
Select one or more PowerServer profiles and Web Server profiles to set up a deployment profile.
-
Easily add, edit, and remove server profiles.
-
Test connections in server profiles. If the connection is successful, it means that the application can be deployed to the server configured in the server profile.
-
Manage which applications are accessible from the PowerServer Toolkit shortcut Run button. The shortcut lists the applications that are deployed to the default server profiles.
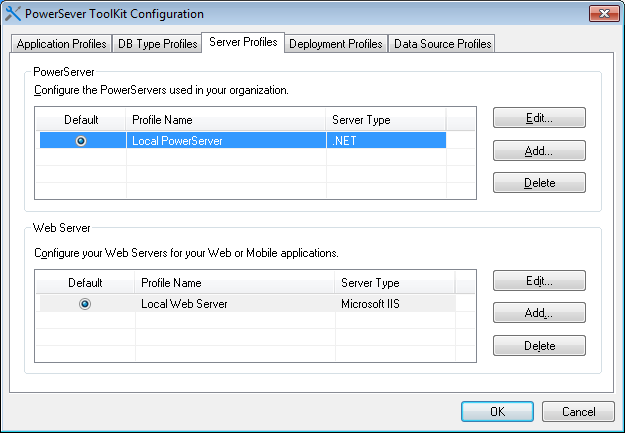
There are two main parts on the Server Profiles tab page, as shown in the following figure. The upper part is for management of PowerServer profiles, while the lower part is for management of Web server profiles.
You can select a PowerServer profile or a Web Server profile as the DEFAULT server profile on the Server Profiles tab page. PowerServer Toolkit's Run shortcut reads the default server profiles and lists the applications that are deployed to default server profiles, enabling you to quickly access them. Applications that are deployed to non-default server profiles are not available in the shortcut. For details about the shortcut, refer to Running PowerServer Applications.
Two sets of Edit, Add, and Delete buttons are available on the Server Profiles tab page for you to modify, create, or remove PowerServer or Web Server profiles. the section called “PowerServer profile settings” and the section called “Web Server profile settings” provide instructions on how to configure the properties for a PowerServer or Web Server profile when you modify or create a new server profile.
Before you edit or add a PowerServer profile, make sure that the PowerServer specified in the profile is running, and that the PowerServer Toolkit computer can successfully connect to the PowerServer computer.
If you want to deploy the application to a PowerServer cluster, you must create profiles for each participating PowerServer and deploy the application to all PowerServer in the cluster.
The following figure shows the PowerServer Profile Configuration window that displays when you click the Edit or Add button in the PowerServer group box of the Server Profiles tab page.
The following table lists detailed instructions on how to specify the properties for a PowerServer profile.
Table 13. PowerServer profile properties
|
|
Property |
Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Profile Settings |
Profile Name |
Assign a name to the PowerServer profile. You should use names that are easy to remember and identify (for example "PowerServer for Test" or "Remote PowerServer"). |
|
PowerServer Settings |
Server Type |
Select J2EE if PowerServer is installed to JBoss, JEUS, WebLogic, or WebSphere; select .NET if PowerServer is installed to Microsoft .NET Framework. |
|
Server |
Enter the IP address or the machine name of the PowerServer. |
|
|
Server Port |
Enter the HTTP or HTTPS port number used by PowerServer. |
|
|
AEM Settings |
AEM URL |
The URL for AEM will be automatically generated after you specify the Server and Server Port. The URL will be in the following format: http://server:port/AEM, (for example, http://localhost:8080/AEM). Note: Do not use a "localhost" listener in a production environment. |
|
Connection method |
Use HTTP or HTTPS (secure) option to connect to PowerServer. |
|
|
Deployment Security Settings |
Deployment Security |
The Get State button can get the state of the Deployment Security settings in AEM. If Deployment Security is set to ON, the state will be "Enabled" and you must specify the deployment user name and password. By default, the Deployment Security in AEM is OFF, so the state is "Disabled". |
|
Username |
Enter the username used to deploy the application. The username and password for the deployment security feature are configured in AEM. The username can be left blank if the deployment security feature is turned off in AEM. |
|
|
Password |
Enter the password used to deploy the application. The username and password for the deployment security feature are configured in AEM. The password can be left blank if the deployment security feature is turned off in AEM. |
After profile configuration, perform the following steps to make sure the PowerServer profile can be successfully used for application deployments:
-
Check whether the deployment security settings are configured correctly. The username and password in the deployment security settings must be the same as those configured in AEM. Make sure you get the correct deployment username and password from the AEM administrator.
-
Test PowerServer settings by clicking the Test PowerServer Settings button. Do NOT proceed to the next step until the testing succeeds.
Before you edit or add a Web Server profile, make sure the Web Server specified in the profile is running and that the PowerServer Toolkit computer can successfully connect to the Web Server computer.
The following figure shows the Web Server Profile Configuration window that displays when you click the Edit or Add button in the Web Server group box of the Server Profiles tab page.
The following table lists detailed instructions for how to specify the properties for a Web Server profile.
Table 14. Instructions for creating a Web Server profile
|
|
Property |
Instructions |
|---|---|---|
|
Profile Settings |
Profile Name |
Assign a name to the Web Server profile. You should use names that are easy to remember and identify such as "Web Server for Test" or "Production Web Server". |
|
File Transfer Type |
Select Local Server if the Web Server is on the local machine. Select FTP Server or SFTP Server if the Web Server is on a machine different from the PowerServer Toolkit machine. |
|
|
Web Server Settings |
Server Type |
Select the Web server type. PowerServer supports the following Web Server types: Apache, IIS, JBoss, WebLogic, WebSphere, and JEUS. |
|
Server |
Enter the IP address or the domain name of Web Server. |
|
|
Server Port |
Enter the HTTP or HTTPS port number of Web Server. |
|
|
Local Server Settings |
Web Root Path |
Enter the home directory of the Web server where the application WAR file will be deployed to. For example: For Apache, the home directory is <apache root>\htdocs For IIS, the home directory is <systemdrive>:\Inetpub\wwwroot; For WildFly and JBoss EAP, the home directory is <jboss root>\standalone\deployments; For WebLogic 8, the home directory is <systemdrive>:\bea\user_projects\domains\appeon_domain\applications; For WebLogic 9/10, the home directory is <systemdrive>:\bea\user_projects\domains\appeon_domain\autodeploy; For WebSphere, the home directory is <systemdrive>:\IBM\WebSphere6\AppServer\installableApps; For JEUS, the home directory is
Note: For WebLogic (started in production mode) and WebSphere, you will need to manually deploy the WAR file in the server administrative control. This is required by the WebLogic and WebSphere, not by PowerServer. It is similar to deploying the PowerServer EAR package; you can follow the instructions in the section called "Deploying appeonserver.ear package" in the Installation Guide. |
|
FTP Settings |
Port |
Enter the FTP server port number. The typical FTP port is port 21. If you use a remote Web Server, PowerServer Toolkit will upload the files to Web Server using FTP protocol. Note that PowerServer Toolkit works as a passive FTP client when uploading files. So you need to make sure that you are using passive FTP and the FTP data port and command port are configured properly in the firewall. |
|
Username |
Enter the username for FTP login. If the FTP server offers anonymous access then the username should be anonymous. |
|
|
Password |
Enter the password for FTP login. If no password is set for the FTP server or the FTP Username is anonymous, leave this field blank. |
|
|
Select this checkbox if you want PowerServer Toolkit to upload the files via FTPS protocol. Make sure the FTP server is configured to "Require SSL Connections" (not "Allow SSL Connections") for the control channel and the data channel. Also, a server SSL certificate should be specified, although PowerServer Toolkit will not verify whether the certificate is signed by a trusted certificate authority, or verify the certificate's name against the host. The supported TLS/SSL protocols include TLSv1.2, TLSv1.1, TLSv1.0, SSLv3, and SSLv2. And the FTP server should not be configured to require the client-side SSL certificate, otherwise PowerServer Toolkit will fail to connect with the server, because PowerServer Toolkit does not support validating the client-side SSL certificate. |
||
|
SFTP Settings |
Port |
Enter the SFTP server port number. The typical SFTP port is port 22. |
|
Username |
Enter the username for SFTP login. |
|
|
Password |
Enter the password for SFTP login. |
|
|
Private key file |
Enter or select the private key file for the SFTP server. |
|
|
Key file passphrase |
Enter the key file passphrase for the SFTP server. |
After the profile configuration, perform the following steps to make sure the Web Server profile can be successfully used for application deployments:
-
Test Web Server settings by clicking the Test Web Server Settings button. Do NOT proceed to the next step until the testing succeeds.
If the Web Server is a remote server, refer to the section called “Two requirements for FTP settings” to make sure the configuration for the Web Server profile is successful.
If the Web Server is an SSL Web server, refer to the section called “If the Web Server is an SSL Web Server” to make sure the configuration for the Web Server profile is successful.
If you configure a Web Server profile for a remote Web Server, make sure the FTP settings in the Web Server profile meet the following two requirements:
-
The user name and password for accessing the FTP server should have permission to read and write files to the FTP server of the Web Server.
-
The FTP home directory should be mapped to the Web root of the Web Server.
The following steps use the Microsoft IIS FTP service as an example to show you how to fulfill the requirements. You should find that the settings for other FTP types are similar to the settings for Microsoft IIS FTP.
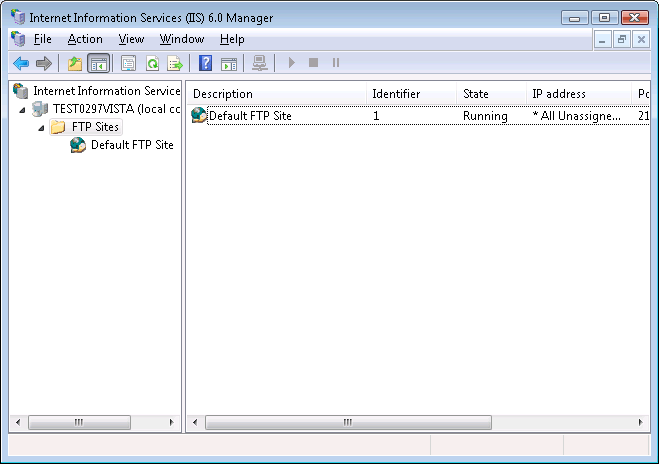
Step 1: On the FTP server (Web Server), open the Internet Services Manager in Administrative Tools, as shown in the following figure.
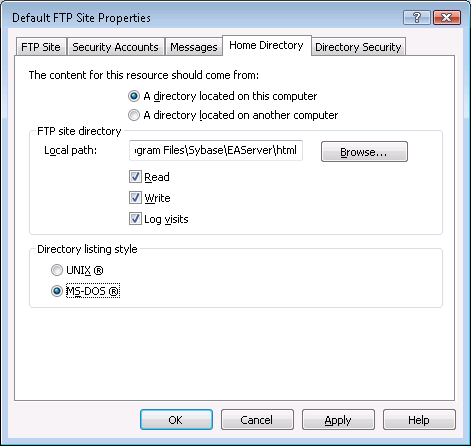
Step 2: Right click on Default FTP Site and select Properties in the popup menu. The Default FTP Site Properties window is displayed.
Step 3: Go to the Home Directory tab and verify that:
-
The Local Path is the full path to the Web Server document root.
-
The Write property of the FTP Site Directory is enabled.
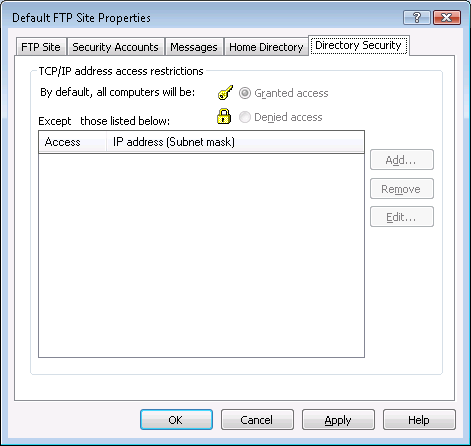
Step 4: Go to the Directory Security tab and verify that the Granted Access option is checked, as shown in the following figure.