- Using the DirectConnect interface
- Supported versions for the DirectConnect interface
- Supported DirectConnect interface datatypes
- Basic software components for the DirectConnect interface
- Preparing to use the database with DirectConnect
- Defining the DirectConnect interface
- Creating the extended attribute system tables in DB2 databases
About this chapter
This chapter describes how to use the DirectConnect interface in PowerBuilder.
The DirectConnect interface uses SAP's Open Client CT-Library (CT-Lib) API to access a database through SAP middleware data access products such as the DirectConnect for OS/390 component of Mainframe Connect and Open ServerConnect.
Accessing Unicode data
PowerBuilder can connect, save, and retrieve data in both ANSI/DBCS and Unicode databases. When character data or command text is sent to the database, PowerBuilder sends a DBCS string if the UTF8 database parameter is set to 0 (the default). If UTF8 is set to 1, PowerBuilder sends a UTF-8 string.
The database server must have the UTF-8 character set installed. See the description of the UTF-8 database parameter in the section called “UTF8” in Connection Reference.
A Unicode database is a database whose character set is set to a Unicode format, such as UTF-8, UTF-16, UCS-2, or UCS-4. All data must be in Unicode format, and any data saved to the database must be converted to Unicode data implicitly or explicitly.
A database that uses ANSI (or DBCS) as its character set might use special datatypes to store Unicode data. Columns with these datatypes can store only Unicode data. Any data saved into such a column must be converted to Unicode explicitly. This conversion must be handled by the database server or client.
SAP DirectConnect is a data access server that provides a standardized middleware interface between your applications and your enterprise data sources. Data access services to a particular database are defined in a DirectConnect server. Since a DirectConnect server can support multiple access services, you can access multiple databases through a single server.
When you use the DirectConnect interface to connect to a particular database, your connection is routed through the access service for that database. An access service consists of a named set of configuration properties and a specific access service library.
To access DB2 data on an IBM mainframe through a DirectConnect server, you can use the DirectConnect interface to connect through either a DirectConnect for MVS access service or a DirectConnect Transaction Router Service (TRS).
TRS provides fast access to a DB2/MVS database by using remote stored procedures. The DirectConnect interface supports both versions of the TRS library: TRSLU62 and TRSTCP.
The DirectConnect server operates in two modes: SQL transformation and passthrough. The DirectConnect interface for DB2/MVS uses passthrough mode, which allows your PowerBuilder application to have direct access to the capabilities of the DB2/MVS data source.
SAP's Open ServerConnect supports mainframe applications that retrieve and update data stored on the mainframe that SAP client applications can execute. Client applications can connect directly to a DB2/MVS database through an Open ServerConnect application residing on the mainframe, eliminating the need for an intermediate gateway like DirectConnect. (This type of connection is also known as a gateway-less connection.) In addition, an Open ServerConnect application presents mainframe Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs) as database stored procedures to the client application.
To access DB2 data on an IBM mainframe through Open ServerConnect, you can use the DirectConnect interface to connect through Open ServerConnect for IMS and MVS.
To select how PowerBuilder accesses the database, use the Choose Gateway drop-down list on the Connection tab of the DirectConnect Database Profile Setup dialog box and select one of the following:
-
Access Service
-
Gatewayless
-
TRS
All the DBParm parameters defined for the DirectConnect interface are applicable to all three connections except the following:
-
HostReqOwner applies to Access Service and Gatewayless only
-
Request, ShowWarnings, and SystemOwner apply to Access Service only
-
UseProcSyntax applies to Gatewayless only
See Database Parameters in Connection Reference for the complete list of DBParm parameters applicable to the DirectConnect interface.
The DirectConnect interface uses a DLL named PBDIR.dll to access a database through either DirectConnect or Open ServerConnect.
Required DirectConnect versions
To access a DB2/MVS database through the access service, it is strongly recommended that you use DirectConnect for MVS access service version 11.1.1p4 or later.
To access a DB2/MVS database through TRS, it is strongly recommended that you use DirectConnect TRS version 11.1.1p4 or later.
For information on DirectConnect for MVS and TRS, see your DirectConnect documentation.
Required Open ServerConnect versions
To access a DB2/MVS database through Open ServerConnect, it is strongly recommended that you use Open ServerConnect IMS and MVS version 4.0 or later.
For information on Open ServerConnect for MVS, see your Open ServerConnect documentation.
The DirectConnect interface supports the PowerBuilder datatypes listed in the following table in DataWindow objects and embedded SQL.
|
Char (fewer than 255 characters) |
Long VarChar |
|
Char for Bit Data |
Real |
|
Date |
SmallInt |
|
Decimal |
Time |
|
Double Precision |
Timestamp (DateTime) |
|
Float |
VarChar |
|
Integer |
VarChar for Bit Data |
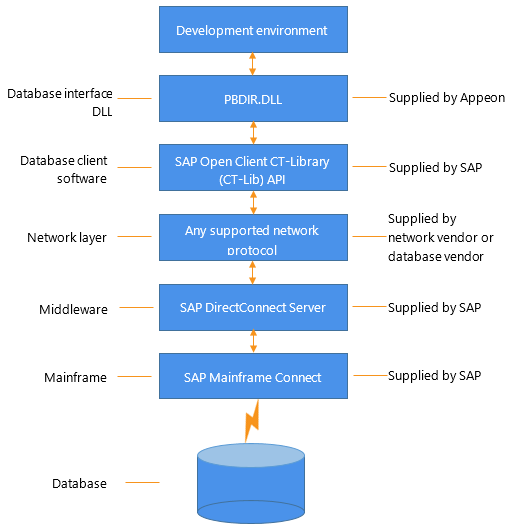
The following figure shows the basic software components required to access a database using the DirectConnect interface and the DirectConnect middleware data access product.
Figure: Components of a DirectConnect connection using DirectConnect middleware
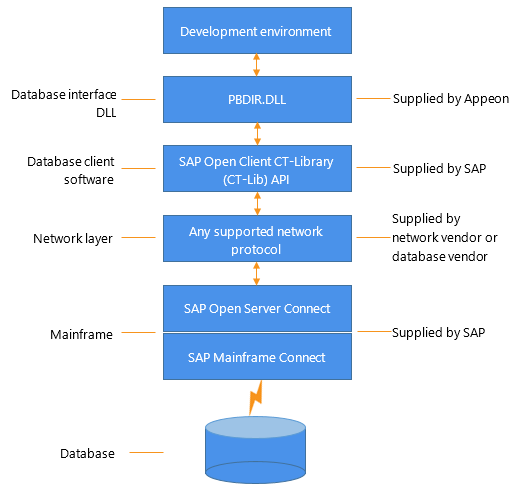
The following figure shows the basic software components required to access a database using the DirectConnect interface and the Open ServerConnect middleware data access product.
Figure: Components of a DirectConnect connection using Open ServerConnect middleware
Before you define the interface and connect to a database through the DirectConnect interface, follow these steps to prepare the database for use:
-
Install and configure the SAP middleware data access products, network, and client software.
-
Install the DirectConnect interface.
-
Verify that you can connect to your middleware product and your database outside PowerBuilder.
-
Create the extended attribute system tables outside PowerBuilder.
Step 1: Install and configure the SAP middleware product
You must install and configure the SAP middleware data access product, network, and client software.
To install and configure the SAP middleware data access product, network, and client software:
-
Make sure the appropriate database software is installed and running on its server.
You must obtain the database server software from your database vendor.
For installation instructions, see your database vendor's documentation.
-
Make sure the appropriate DirectConnect access service software is installed and running on the DirectConnect server specified in your database profile
or
Make sure the appropriate Open ServerConnect software is installed and running on the mainframe specified in your database profile.
-
Make sure the required network software (such as TCP/IP) is installed and running on your computer and is properly configured so you that can connect to the DirectConnect server or mainframe at your site.
You must install the network communication driver that supports the network protocol and operating system platform you are using.
For installation and configuration instructions, see your network or database administrator.
-
Install the required Open Client CT-Library (CT-Lib) software on each client computer on which PowerBuilder is installed.
You must obtain the Open Client software from SAP. Make sure the version of Open Client you install supports both of the following:
The operating system running on the client computer
The version of PowerBuilder that you are running
Open Client required
To use the DirectConnect interface, you must install Open Client.
For information about Open Client, see your Open Client documentation.
-
Make sure the Open Client software is properly configured so you can connect to the middleware data access product at your site.
Installing the Open Client software places the SQL.INI configuration file in the SQL Server directory on your computer. SQL.INI provides information that SQL Server uses to find and connect to the middleware product at your site. You can enter and modify information in SQL.INI with the configuration utility or editor that comes with the Open Client software.
For information about editing the SQL.INI file, see Editing the SQL.INI file. For more information about setting up SQL.INI or any other required configuration file, see your SQL Server documentation.
-
If required by your operating system, make sure the directory containing the Open Client software is in your system path.
-
Make sure only one copy of each of the following files is installed on your client computer:
-
DirectConnect interface DLL
-
Network communication DLL (such as NLWNSCK.DLL for Windows Sockets-compliant TCP/IP)
-
Open Client DLLs (such as LIBCT.DLL and LIBCS.DLL)
-
Step 2: Install the interface
If you install PowerBuilder using the PowerBuilder Installer (an online setup program), the Direct Connect Interface (DIR) is automatically installed. If you install PowerBuilder using the downloaded installation package (an offline setup program), select Native Database Interfaces | Direct Connect Interface (DIR) from the list of components.
Step 3: Verify the connection
Make sure you can connect to your middleware product and your database and log in to the database you want to access from outside PowerBuilder.
Some possible ways to verify the connection are by running the following tools:
-
Accessing the database server
Tools such as the Open Client/Open Server Configuration utility (or any Ping utility) check whether you can reach the database server from your computer.
-
Accessing the database
Tools such as ISQL or SQL Advantage (interactive SQL utilities) check whether you can log in to the database and perform database operations. It is a good idea to specify the same connection parameters you plan to use in your PowerBuilder database profile to access the database.
Step 4: Create the extended attribute system tables
PowerBuilder uses a collection of five system tables to store extended attribute information. When using the DirectConnect interface, you must create the extended attribute system tables outside PowerBuilder to control the access rights and location of these tables.
Run the DB2SYSPB.SQL script outside PowerBuilder using the SQL tool of your choice.
For instructions, see Creating the extended attribute system tables in DB2 databases.
Make sure the SQL.INI file provides an entry about either the access service being used and the DirectConnect server on which it resides or the Open ServerConnect program being used and the mainframe on which it resides.
For the server object name, you need to provide the exact access service name as it is defined in the access service library configuration file on the DirectConnect server. You must also specify the network communication DLL being used, the TCP/IP address or alias used for the DirectConnect server on which the access service resides, and the port on which the DirectConnect server listens for requests:
[access_service_name] query=network_dll,server_alias,server_port_no
PowerBuilder users must also specify the access service name in the SQLCA.ServerName property of the Transaction object.
To define a connection through the DirectConnect interface, you must create a database profile by supplying values for at least the basic connection parameters in the Database Profile Setup - DirectConnect dialog box. You can then select this profile anytime to connect to your database in the development environment.
For information on how to define a database profile, see Using database profiles.
This section describes how PowerBuilder creates the extended attribute system tables in your DB2 database to store extended attribute information. It then explains how to use the DB2SYSPB.SQL script to create the extended attribute system tables outside PowerBuilder.
You can use the DB2SYSPB.SQL script if you are connecting to the IBM DB2 family of databases through any of the following database interfaces:
-
ODBC interface
-
SAP DirectConnect interface
When you create or modify a table in PowerBuilder, the information you provide is stored in five system tables in your database. These system tables contain extended attribute information such as the text to use for labels and column headings, validation rules, display formats, and edit styles. (These system tables are different from the system tables provided by your DB2 database.)
By default, the extended attribute system tables are created automatically the first time a user connects to the database using PowerBuilder.
When you use the DirectConnect interface
When you use the DirectConnect interface, the extended attribute system tables are not created automatically. You must run the DB2SYSPB.SQL script to create the system tables as described in Using the DB2SYSPB.SQL script.
To ensure that the extended attribute system tables are created with the proper access rights:
-
Make sure the first person to connect to the database with PowerBuilder has sufficient authority to create tables and grant permissions to PUBLIC.
This means that the first person to connect to the database should log in as the database owner, database administrator, system user, system administrator, or system owner, as specified by your DBMS.
Why do this
If you are a system administrator at a DB2 site, you might prefer to create the extended attribute system tables outside PowerBuilder for two reasons:
-
The first user to connect to the DB2 database using PowerBuilder might not have the proper authority to create tables.
-
When PowerBuilder creates the extended attribute system tables, it places them in the default tablespace. This might not be appropriate for your needs.
When using the DirectConnect interface
You must create the extended attribute system tables outside PowerBuilder if you are using the DirectConnect interface. You need to decide which database and tablespace should store the system tables. You might also want to grant update privileges only to specific developers or groups.
What you do
To create the extended attribute system tables, you run the DB2SYSPB.SQL script outside PowerBuilder. This script contains SQL commands that create and initialize the system tables with the table owner and tablespace you specify.
Where to find DB2SYSPB.SQL
The DB2SYSPB.SQL script is in the Server directory in the PowerBuilder setup program. This directory contains server-side installation components and is not installed with PowerBuilder on your computer.
You can access the DB2SYSPB.SQL script by copying it to your computer.
Use the following procedure from the database server to create the extended attribute system tables in a DB2 database outside PowerBuilder. This procedure assumes you are accessing the DB2SYSPB.SQL script from d:\server.
To create the extended attribute system tables in a DB2 database outside PowerBuilder:
-
Log in to the database server or gateway as the system administrator.
-
Use any text editor to modify d:\server\DB2SYSPB.SQL for your environment. You can do any of the following:
-
Change all instances of PBOwner to another name.
Specifying SYSIBM is prohibited
You cannot specify SYSIBM as the table owner. This is prohibited by DB2.
-
Change all instances of database.tablespace to the appropriate value.
-
Add appropriate SQL statement delimiters for the tool you are using to run the script.
-
Remove comments and blank lines if necessary.
PBCatalogOwner
If you changed PBOwner to another name in the DB2SYSPB.SQL script, you must specify the new owner name as the value for the PBCatalogOwner DBParm parameter in your database profile. For instructions, see PBCatalogOwner in the section called “PBCatalogOwner” in Connection Reference.
-
-
Save any changes you made to the DB2SYSPB.SQL script.
-
Execute the DB2SYSPB.SQL script from the database server or gateway using the SQL tool of your choice.