Working with PowerScript Migrator
Last Updated: August 2022
Steps for migrating PowerScript to C#
To migrate PowerScript to C#,
- Open an existing project in SnapDevelop, or create a new one. SnapDevelop will not allow you to open a PB workspace until you have created a C# project.
- Right click on the solution name in the Solution Explorer and then select Open PB Workspace.
- Right click on an object under the imported PB workspace and then select Translate Selected Item.
The original PowerScript and the translated code of the object will display in the editor side by side.
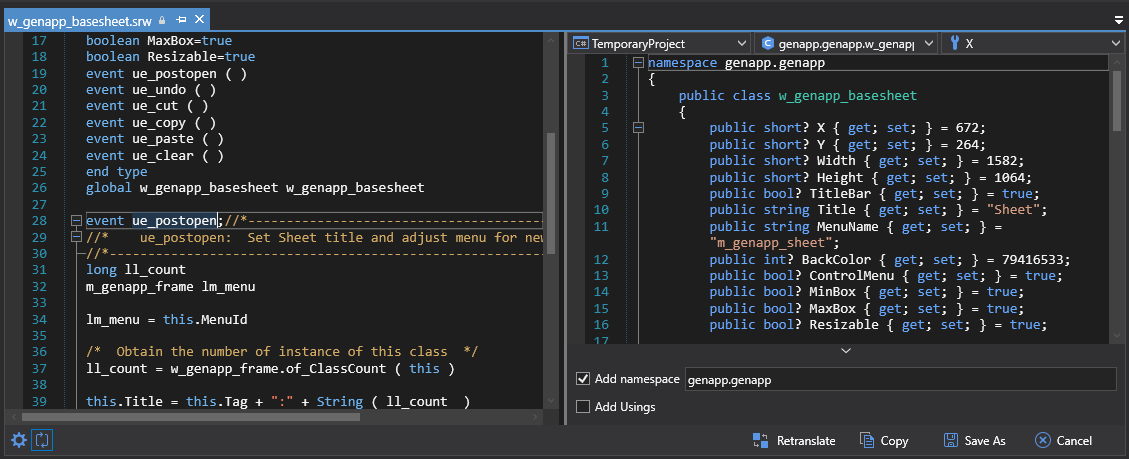
You can also translate multiple objects at the same time. To do so, you can right click on a .pbl or .pbt file, and select Batch Translate. Or you can select multiple objects using the Shift key, and then select Batch Translate in the context menu.
To view the PowerScript and the translated code for a method, you can place the cursor in the method in one editor, then the other editor will automatically scroll to locate the corresponding method and highlight the method name. You can turn off this feature by de-selecting the Highlight Matching Method icon ( ).
).
If the current object has referenced other objects which have not been translated before, you should translate the referenced objects first so that the current object can be translated with accurate data type. You can click the Translate Referenced Objects First icon ( ) and then select the referenced object. After translating all of the referenced objects, go back to the current object and translate it again (using the Retranslate button).
) and then select the referenced object. After translating all of the referenced objects, go back to the current object and translate it again (using the Retranslate button).
Although you cannot edit the code in the editor, you can add class definition, namespace, and the using statements to the translated code.
In the PowerScript editor on the left, you can also translate a portion of the code by right-clicking and selecting Translate and Copy to Clipboard or Translate and Open in Editor.
Options for migrating PowerScript to C#
You can click the Settings icon ( ) at the bottom of the editor or select the Tools | Options menu to open the options window for PowerScript Migrator. You can configure how you would like to translate the array, Any type, event, and other translation settings.
) at the bottom of the editor or select the Tools | Options menu to open the options window for PowerScript Migrator. You can configure how you would like to translate the array, Any type, event, and other translation settings.
Translate the array to
- C# array type -- (default) Fixed-length arrays will be translated to C# array, and variable-length arrays will be translated to PbArray. PbArray is a custom array type defined in PowerScript.Bridge.
- PbArray -- All arrays will be translated to PbArray. Fixed-length arrays will use ArrayEx.CreateInstance method to process the default value for nullable types. The C# array will be initialized in the .NET way, for example, two-dimensional arrays are assigned with values horizontally, missing data will be populated automatically, redundant data will be discarded. Value assignments between arrays will use the ArrayEx.Assign method.
Translate Any type to
- C# object type -- The Any data type will be translated to C# object type.
- C# dynamic -- The Any data type will be translated to C# dynamic. If you translate Any data type to C# dynamic, no compiler diagnostic would be provided for the related code.
Translate the event to
- A method -- (default) the events will be translated to C# methods.
- A C# event that uses EventArgs for its parameter or return value -- all events will be translated to C# events. The event that has no parameter and return value is always translated to the C# event (similar to this: void xxxHandler(object sender, EventArgs args)). If the event has parameter or return value, the C# event will use EventArgs for the parameter and return value.
Other translation settings
- Whether to translate the basic type to be nullable.
- Whether to add informative comments to the translated code. The comments will be tagged with INFO.
- Whether to add comments to the code that may be inaccurately translated. The comments will be tagged with WARN.
- Whether to add comments to the code that may be erroneously translated. The comments will be tagged with ERROR.
- Whether to output SqlCode of the SELECT statement in SqlResult parameter when a query is run.
Rules for migrating PowerScript to C#
PowerScript Migrator is to translate PowerScript to C# language which is native C# language and compliant with C# conventions, and less dependent on the runtime library.
Currently, the translation is mainly performed to the common usages of basic data types, DataStores, and embedded SQLs, although the PowerBuilder visual objects will also be translated, however, they cannot be used in C#.
Keep in mind the following basics of C# syntax: 1) the C# language is case sensitive, 2) index starts from 0, 3) only one variable can be defined in one line, 4) characters are included in single quotation marks, 5) strings are included in double quotation marks.
Modifier keywords
Modifier keywords are used to modify declarations of types (class, struct, interface, enum) and type numbers (fields, properties, methods, indexers, ...)
PowerBuilder modifiers will be translated to the C# modifiers according to the following table.
Table 1:
| PowerBuilder modifier | C# modifier |
|---|---|
| Global/ Public | public |
| Protected | protected |
| Private | private |
| Other modifiers | internal |
Structures
PowerBuilder objects inherited from structure are first translated to C# classes. Users can choose to translate them to C# structures (struct). The elements of a structure will be translated to C# properties. But note that the C# structure (struct) does not support properties to be assigned with default values.
Objects
All PowerBuilder objects (except structures) will be translated to C# classes.
The variables of an object will be translated to C# fields.
The PowerBuilder variables that are declared in different scopes (Global/Shared/Instance) will be translated to C# fields according to the following table.
Table 2:
| PowerBuilder variables | C# fields |
|---|---|
| Global variables | Public static fields |
| Shared variables | Protected fields |
| Instance variables | Public fields |
If the modifier is explicitly used, then it will be translated according to table 1.
If the constant modifier is used, it will be translated to C# const modifier.
Header
If the translation is performed within the object header (including object declaration/definition, internal object declaration/definition, variable and prototype definition), then the current object, internal objects, and variables will all be translated.
NVO
The entire script file (.sru) of NVO will be translated.
Auto-initialization
If the variable is declared as a structure, internal object, or auto-instantiated object, and is not assigned with an initial value, then the default object will be created and assigns a value to the variable.
Translation cache
When translating a piece of code which uses 1) untranslated objects as base class, variable type, or parameter type, 2) unknown variables or functions, the migrator would recommend users first translate the object/script on which the current code has dependency. The translation will be cached under the current workspace folder, and will be restored when the workspace is opened next time, if the same object/script is translated again, the cached translation will be overwritten by the new translation. You can clear the cache by right-clicking the workspace and selecting Clear Translation Cache.
Dot notation translation
When translating a piece of code, the migrator would prompt users to first translate the script referenced by the dot notation, and cache the translation of the referenced property, variable, method etc. (no matter how deep the dot notation chain will be) and finally figure out the correct data types based on the cache. This can ensure the translation correctness of the code in the whole dot notation chain.
For example:
Suppose there are objects A, B, and C.
A defines a variable a of type B; B defines an attribute c of type C; C defines a method func (double d).
Now that the user is translating the following code, but has not translated objects A, B, and C before.
A la
la.b.C.func (3.3)
In this case, the migrator will prompt the user to translate object A first; when translating object A, the migrator will prompt user to translate object B first, and the outline information of object A will be cached; when translating object B, the migrator will prompt user to translate object C first, and the outline information of object B will be cached; after object C is translated, the outline information of object C will be cached as well.
After translating objects A, B and C, now the migrator translates the above code.
The first statement A la is translated to A la = null; and the local variable la is recorded in the translation context.
For the second statement: the first notation la will be recognized as a local variable and the type is A according to the context; the second notation .b will be recognized as a variable defined on object A and the type is B according to the cache; the third notation .C will be recognized as an attribute defined on object B and the type is C and the attribute reference is modified to c; for the fourth notation .func (3.3), the migrator will first translate the parameter 3.3 to 3.3M, and then the migrator matches the method in the cache and finds that func is a method defined on type C, which contains a parameter d of type double, so the migrator modify the parameter 3.3M to 3.3D, and come to the translation func (3.3D).
Finally, the above code will be translated to:
A la = null;
la.b.c.func (3.3D);
Inherited members
When translating a piece of code in the recommended order, the migrator can also find the members (object, method etc.) in the parent object, to ensure the inherited members are translated correctly.
Global variables
When loading the workspace, the migrator will translate the application definition, and cache the translation, to ensure the reference to the global variables in the entire workspace can be correctly translated.
Events
Events can be translated in two ways. Users can specify the way in the Options dialog.
#1 (default): The event will be translated to C# method, except for events that have no parameter and return value which are always translated to the C# event (similar to this: void xxxHandler(object sender, EventArgs args))
#2: The event will be translated to C# event. If the event has parameter definition, the C# event will create a type inherited from EventArgs. The parameter definition will be defined in the property of this type, and any reference to the parameter will be changed to the reference to the property.
Functions
Functions will be translated to C# methods. The modifier will be translated according to Table 1.
The global function will be translated to a public static method, as a member of the GlobalFunc class (a public static partial class).
Statements
Statements will be translated to C# statements according to the following table.
Table 3:
| PowerScript statements | C# statements |
|---|---|
| destroy | Dispose method |
| if elseif else/oneline if/pound if) | if elseif else |
| choose case else | switch case |
| do loop while/until | do while |
| do while loop/until | while |
| for | for |
| try catch finally | Try catch finally |
| label | label |
| call | (call directly) |
| goto | goto |
| exist | break |
| continue | continue |
| return | return |
| create | new |
| throw | throw |
Comments
The migrator will translate the comments and blanks as best as possible, to preserve the readability of the scripts.
The migrator will also add the following comments, to help users locate and read scripts:
- Informative comments (INFO), for example, descriptive text to a piece of code.
- Comments (WARN) that warn users the translation may not be accurate or the possible areas that may need manual adjustment.
- Comments (ERROR) that tell users translation errors may exist.
Users can select whether to add these comments in the Options dialog.
The following table shows the code for informative comments (INFO).
Table 4:
| Type | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Basic syntax (00) | INFO0000 | Return. |
| Embedded SQL (01) | INFO0100 | Embedded SQL. |
| INFO0101 | Cursor declaration: {0}. | |
| INFO0102 | Open dynamic cursor: {0}. | |
| INFO0103 | Stored procedure declaration: {0}. | |
| INFO0104 | Dynamic procedure execution: {0}. | |
| INFO0105 | Dynamic sql execution. | |
| INFO0106 | Open connection. | |
| INFO0107 | Close connection. | |
| INFO0108 | Commit transaction. | |
| INFO0109 | Rollback transaction. | |
| INFO0110 | Fetch {0}. | |
| INFO0111 | Close {0}. |
The following table shows the code for comments (WARN).
Table 5:
| Type | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| basic syntax (00) | WARN0000 | Double check the translation of post call '{0}'. |
| WARN0001 | Double check the translation of dynamic call '{0}'. | |
| WARN0002 | The properties of the structure do not support initialization({0}). | |
| WARN0003 | Remove the statement if you do not want to manually release the object. | |
| WARN0004 | Double check the translation of array subscript may be inaccurate. | |
| WARN0005 | Double check the translation of the {0}the parameter. It is an index parameter. | |
| WARN0006 | Double check the translation of the for variable '{0}'. | |
| WARN0007 | Double check the translation of the function '{0}' and the code that uses its return value, because the return value is an index. | |
| DataStore (02) | WARN0200 | Function '{0}' has been translated into property({1}). If any code uses its return value, please adjust the code. |
The following table shows the code for comments (ERROR).
Table 6:
| Type | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Basic syntax (00) | ERROR0000 | Need to reprocess the index reference ({0} to {1}) in the array({li_arr}). |
| ERROR0001 | The for expression is invalid. | |
| ERROR0002 | Not a valid binary expression. | |
| ERROR0003 | Not a valid unary expression. | |
| ERROR0004 | Not a valid unary or binary expression. | |
| ERROR0005 | Be sure to use the full name of the type. | |
| ERROR0006 | Replace the object with a real type. | |
| ERROR0007 | Syntax error. | |
| ERROR0008 | Translation of the enum value({0}) is not supported. | |
| ERROR0009 | Translation of the cast({0}) is not supported. | |
| ERROR0010 | The method name duplicates with an existing class name. Please change the method name. | |
| Embedded SQL (01) | ERROR0100 | Replace ' |
| ERROR0101 | Not a valid sqlca expression. | |
| ERROR0102 | Missing a prepare statement. | |
| ERROR0103 | Missing a fetch statement. | |
| ERROR0104 | Missing a dynamic procedure/cursor declaration statement. | |
| ERROR0105 | Embedded SQL statement syntax error. | |
| DataStore (02) | ERROR0200 | Translation of the data expression at the end of the Selected is not supported. |
| ERROR0201 | Verify whether the dwitemstatus is PropertyState or shall be changed to ModelState. | |
| ERROR0202 | DataFormat.Text is temporarily used to replace the unsupported '{0}' saveastype. |
Index
PowerBuilder index starts from 1, while C# index starts from 0. Therefore, the index in the following areas will minus 1 when used literally:
- access to array index
- index parameter in C# method
- variable in For loops
- relational operations with index
- arithmetic operations with index
If the index is used in a calculation in which function is called, the index will not minus 1, because the function is supposed to return a result which is C# compliant.
The "minus 1" method might turn out wrong under some conditions, therefore, these areas will be added with comments to remind users to double check that the index is correct.
Expressions
A local variable will be translated to C# variable (only one variable can be defined in one line) and the variable will be assigned with an initial value.
Other expressions will be translated according to the following table.
Table 7:
| Expression Types | Examples |
|---|---|
| Unary operation | x++, x--, +x, -x |
| Arithmetic operation | +, -, *, /, %, ^ |
| Relational operation | =, <>, >, <, >=, <= |
| Logical operation | and, or, xor, >>, << |
| Assignment operation | =, +=, -=, *=, /=, ^= |
| Array access | xx[0] |
| Member access | xx.xx |
| Array initialization | {xx, xx} |
| Type conversion | datatype(expr) |
| Method/event calls | x(), event x() |
| Literal | 1, '2', "3" |
Datatype conversion
Unlike PowerBuilder which allows conversions between numeric data types, C# has quite strict controls over this. For data types that are not allowed to convert to other data type implicitly in C#, the migrator may do forced conversions based on its deduction of data type.
Basic types
Basic data types will be directly translated into the corresponding C# data types.
PowerBuilder allows the numeric value to be null, therefore, numeric types will be translated to the C# nullable types. Users can select not to translate to nullable type in the Options dialog.
Table 8:
| PowerBuilder Types | C# Types |
|---|---|
| integer/int | short? |
| unsignedinteger/unsignedint/uint | ushort? |
| long | int? |
| Unsignedlong/ulong | uint? |
| longlong | long? |
| byte | byte? |
| char/character | char? |
| boolean | bool? |
| dec/decimal/dec{x}/decimal{x} | decimal? |
| real | float? |
| double | double? |
| date | DateTime? |
| time | TimeSpan? |
| datetime | DateTime? |
| string | string |
| any | object/dynamic |
| blob/blob{x} | PbBlob |
The special usage of date types in PowerScript will be translated to the C# ParseExact method of the corresponding type. For example,
ld_41 = 2003-03-03 // ld_41 = DateTime.ParseExact("2003-03-03", "yyyy-MM-dd", null);
lt_21 = 12:12:12 // lt_21 = TimeSpan.ParseExact("23:23:23.230", "g", null);
Arrays can be translated in two ways. Users can specify the way in the Options dialog.
- #1 (default): Fixed-length arrays will be translated to C# array, and variable-length arrays will be translated to PbArray.
- #2: All arrays will be translated to PbArray. Fixed-length arrays will use ArrayEx.CreateInstance method to process the default value for nullable types. The C# array will be initialized in the .NET way, for example, two-dimensional arrays are assigned with values horizontally, missing data will be populated automatically, redundant data will be discarded. Value assignments between arrays will use the ArrayEx.Assign method.
2- or more-dimensional arrays are unsupported currently.
PowerObject type will be translated to C# object type.
Any type will be translated to C# object type by default. Users can select to translate to dynamic type in the Options dialog.
Exception type will be translated to C# Exception type, and GetMessage method and Text property will be translated to Message property; SetMessage method will be translated to the Exception object which is re-instantiated.
PowerScript:
Exception lex_delete
lex_delete = create Exception
lex_delete.SetMessage("Nothing deleted.")
C# scripts:
Exception lex_delete = null;
lex_delete = new Exception();
lex_delete= new Exception("Nothing deleted.");
Nullable type conversion
As mentioned above, basic types will be translated to nullable types in C#. However, the runtime APIs and the C# native interfaces accept only non-nullable types. The migrator will do forced conversions between nullable types and non-nullable types based on its deduction of types and handle the property/method calls for nullable types.
Enumeration
PowerBuilder dwitemstatus enumerated values will be translated to C# PropertyState enumerated values, as shown in the following table.
Table 9:
| PB dwitemstatus enumerated value | C# PropertyState/ModelState enumerated value |
|---|---|
| new! | ModelState.New |
| newmodified! | ModelState.NewModified |
| notmodified! | PropertyState.NotModified |
| datamodified! | PropertyState.Modified |
PowerBuilder dwbuffer enumerated values will be translated to C# DwBuffer enumerated values, as shown in the following table.
Table 10:
| PB dwbuffer enumerated value | C# DwBuffer enumerated value |
|---|---|
| primary! | Primary |
| delete! | Delete |
| filter! | Filter |
PowerBuilder parmtype enumerated values will be translated to C# PbDataType enumerated values, as shown in the following table.
Table 11:
| PB parmtype enumerated value | C# PbDataType enumerated value |
|---|---|
| typeboolean! | Boolean |
| typebyte! | Byte |
| typedate! | Date |
| typedatetime! | DateTime |
| typedecimal! | Decimal |
| typedouble! | Double |
| typeinteger! | Int |
| typelong! | Long |
| typelonglong! | LongLong |
| typereal! | Real |
| typestring! | String |
| typetime! | Time |
| typeuint! | UInt |
| typeulong! | ULong |
| typeunknown! | Unknown |
PowerBuilder saveastype enumerated values will be translated to C# DataFormat enumerated values, as shown in the following table.
Table 12:
| PB saveastype enumerated value | C# DataFormat enumerated value |
|---|---|
| xml! | Xml |
| text! | Text |
| excel! | Text |
| csv! | Text |
| sylk! | Text |
| wks! | Text |
| wk1! | Text |
| dif! | Text |
| dbase2! | Text |
| dbase3! | Text |
| sqlinsert! | Text |
| clipboard! | Text |
| psreport! | Text |
| wmf! | Text |
| htmltable! | Text |
| excel5! | Text |
| xslfo! | Text |
| pdf! | Text |
| excel8! | Text |
| emf! | Text |
| xlsx! | Text |
| xlsb! | Text |
PowerBuilder encoding enumerated values will be translated to C# Encoding enumerated values, as shown in the following table.
Table 13:
| PB encoding enumerated value | C# Encoding enumerated value |
|---|---|
| encodingansi! | ASCII |
| encodingutf8! | UTF8 |
| encodingutf16le! | Unicode |
| encodingutf16be! | BigEndianUnicode |
Global functions
Global functions can be translated in two ways:
#1: if the global function is for a specific type, then it will be translated as an instance of that type, such as blobedit. See table 14 for the translation rule.
#2: The global function is translated as the corresponding static method. If it is supported in the C# base library, then it will be translated to the base library, otherwise, it will be translated to PbGlobal. See table 15 for the translation rule.
Compatible parameter declaration
Considering that PowerBuilder allows a wide range of data type conversions, the global functions in Bridge are declared as type compatible on the number parameter; each has three overloading functions long/double/decimal, to ensure that the translated code can run directly without needing a lot of manual changes.
The following global functions will be translated specially.
Mod -- translated as %.
SetNull -- translated as == null.
IsValid -- translated as != null.
IsNull -- translated as == null.
Today -- translated as DateTime.Now.Date.
Rand/Randomize -- translated as C# type Random.
PowerScript:
int li_r = rand(10)
randomize(88)
li_r = rand(10)
C# scripts:
short? li_r = new Random().Next(10);
var random = new Random(88);
li_r = random.Next(10);
Table 14:
The functions in bold text are translated as C# native code.
| PB global function | C# Type | Method/Property |
|---|---|---|
| len | String | Length (property) |
| lenw | String | Length (property) |
| date | DateTime | Date (property) |
| hour | DateTime | Hour (property) |
| day | DateTime | Day (property) |
| month | DateTime | Month (property) |
| year | DateTime | Year (property) |
| minute | TimeSpan | Minutes (property) |
| second | TimeSpan | Seconds (property) |
| hour | TimeSpan | Hours (property) |
| today | DateTime | Now.Date (property) |
| now | DateTime | Now.Date.TimeOfDay (property) |
| trim | String | Trim |
| lefttrim | String | TrimStart |
| righttrim | String | TrimEnd |
| lower | String | ToLower |
| upper | String | ToUpper |
| trimw | String | Trim |
| lefttrimw | String | TrimStart |
| righttrimw | String | TrimEnd |
| fill | String | Fill |
| filla | String | FillA |
| asc | String | Asc |
| asca | String | AscA |
| isallarabic | String | IsAllArabic |
| isallhebrew | String | IsAllHebrew |
| isanyarabic | String | IsAnyArabic |
| isanyhebrew | String | IsAnyHebrew |
| isarabic | String | IsArabic |
| isarabicandnumbers | String | IsArabicAndNumbers |
| ishebrew | String | IsHebrew |
| ishebrewandnumbers | String | IsHebrewAndNumbers |
| isnumber | String | IsNumber |
| istime | String | IsTime |
| isdate | String | IsDate |
| lastpos | String | LastPos |
| left | String | Left |
| lefta | String | LeftA |
| right | String | Right |
| righta | String | RightA |
| lena | String | LenA |
| match | String | Match |
| mid | String | Mid |
| mida | String | MidA |
| pos | String | Pos |
| posa | String | PosA |
| replace | String | Replace |
| replacea | String | ReplaceA |
| reverse | String | Reverse |
| wordcap | String | WordCap |
| fillw | String | Fill |
| leftw | String | Left |
| midw | String | Mid |
| posw | String | Pos |
| replacew | String | Replace |
| rightw | String | Right |
| matchw | String | Match |
| blobedit | PbBlob | BlobEdit |
| blobmid | PbBlob | BlobMid |
| getbyte | PbBlob | GetByte |
| getbytearray | PbBlob | GetByteArray |
| setbyte | PbBlob | SetByte |
| long | String/PbBlob | Long |
| longlong | String/PbBlob | LongLong |
| byte | String/PbBlob | Byte |
| char | String/PbBlob | Char |
| chara | String/PbBlob | CharA |
| dec | String/PbBlob | Dec |
| double | String/PbBlob | Double |
| real | String/PbBlob | Real |
| integer | String/PbBlob | Integer |
| lowerbound | Array/PbArray | GetLowerBound |
| upperbound | Array/PbArray | GetUpperBound |
| date | String/PbBlob | Date |
| datetime | String/PbBlob | DateTime |
| daysafter | DateTime | DaysAfter |
| dayname | DateTime | DayName |
| daynumber | DateTime | DayNumber |
| relativedate | DateTime | RelativeDate |
| relativetime | TimeSpan | RelativeTime |
| secondsafter | TimeSpan | SecondsAfter |
| string | TimeSpan/DateTime/PbBlob | ToString |
| time | DateTime/PbBlob/String | Time |
Table 15:
The functions in bold text are translated as C# native code.
| PB global function | C# type | Method of the type |
|---|---|---|
| blob | PbBlob | Create |
| today | PbGlobal | Today |
| now | PbGlobal | Now |
| rgb | PbGlobal | RGB |
| ishebrew | PbGlobal | IsHebrew |
| isarabic | PbGlobal | IsArabic |
| byte | PbGlobal | Byte |
| char | PbGlobal | Char |
| chara | PbGlobal | CharA |
| string | PbGlobal | String |
| time | PbGlobal | Time |
| date | PbGlobal | Date |
| datetime | PbGlobal | DateTime |
| integer | PbGlobal | Integer |
| inthigh | PbGlobal | IntHigh |
| intlow | PbGlobal | IntLow |
| long | PbGlobal | Long |
| longlong | PbGlobal | Long |
| real | PbGlobal | Real |
| double | PbGlobal | Double |
| dec | PbGlobal | Dec |
| fact | PbGlobal | Fact |
| int | PbGlobal | Int |
| round | PbGlobal | Round |
| truncate | PbGlobal | Truncate |
| asc | PbGlobal | Asc |
| asca | PbGlobal | AscA |
| space | PbGlobal | Space |
| sign | Math | Sign |
| asin | Math | Asin |
| tan | Math | Tan |
| sin | Math | Sin |
| abs | Math | Abs |
| acos | Math | Acos |
| atan | Math | Atan |
| ceiling | Math | Ceiling |
| cos | Math | Cos |
| cosh | Math | Cosh |
| exp | Math | Exp |
| log | Math | Log |
| logten | Math | Log10 |
| max | Math | Max |
| min | Math | Min |
| sqrt | Math | Sqrt |
| fileexists | File | Exists |
| filecopy | File | Copy |
| filemove | File | Move |
| filedelete | File | Delete |
| directoryexists | Directory | Exists |
| removedirectory | Directory | Delete |
| createdirectory | Directory | CreateDirectory |
| getcurrentdirectory | Directory | GetCurrentDirectory |
| garbagecollect | GC | Collect |
DataStores
DataStore events will be translated to the C# DataStore events according to the following table.
Table 16:
| PB DataStore events | C# DataStore events | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| retrievestart | RetrieveStart | |
| retrieveend | RetrieveEnd | |
| updatestart | UpdateStart | |
| updateend | UpdateEnd |
DataStore properties will be translated to the C# DataStore properties according to the following table.
Table 17:
| PB DataStore properties | C# DataStore properties | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| dataobject | DataObject | |
| object | DwMeta |
DataStore functions will be translated to the C# DataStore properties/methods according to the following table.
Table 18:
| PB DataStore functions | C# DataStore properties/methods | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| rowcount | RowCount | Translated as a property |
| deletedcount | DeletedCount | Translated as a property |
| modifiedcount | ModifiedCount | Translated as a property |
| filteredcount | FilteredCount | Translated as a property |
| retrieve | Retrieve | |
| update | Update | |
| reselectrow | ReselectRow | |
| find | FindIndex | |
| getchild | GetChild | |
| getitemdate | GetItemDate | |
| getitemdatetime | GetItemDateTime | |
| getitemdecimal | GetItemDecimal | |
| getitemstatus | GetItemStatus | |
| getitemstring | GetItemString | |
| getitemtime | GetItemTime | |
| getrowfromrowid | GetRowFromRowId | |
| getrowidfromrow | GetRowIdFromRow | |
| insertrow | InsertRow | |
| getsqlselect | GetSqlSelect | |
| getvalidate | GetValidate | |
| getitemnumber | GetItem | |
| setitem | SetItem | |
| setsort | SetSort | |
| setfilter | SetFilter | |
| sort | Sort | |
| rowsmove | RowsMove | |
| rowsdiscard | RowsDiscard | |
| rowscopy | RowsCopy | |
| resetupdate | ResetUpdate | |
| setsqlselect | SetSqlSelect | |
| settrans | SetDataContext | |
| settransobject | SetDataContext | |
| filter | Filter | |
| deleterow | DeleteRow | |
| setitemstatus | SetItemStatus | |
| setvalidate | SetValidate | |
| setvalue | SetItem | |
| getvalue | GetItem | |
| setsqlpreview | SetSqlSelect | |
| classname | ClassName | |
| exportjson | ExportJson | |
| exportrowasjson | ExportRowAsJson | |
| importjson | ImportJson | |
| importjsonbykey | ImportJsonByKey | |
| importrowfromjson | ImportRowFromJson | |
| importstring | ImportString | |
| importfile | ImportFile | |
| getnextmodified | GetNextModified | |
| reset | Reset | |
| classname | ClassName | |
| exportjson | ExportJson | |
| exportrowasjson | ExportRowAsJson | |
| importjson | ImportJson | |
| importjsonbykey | ImportJsonByKey | |
| importrowfromjson | ImportRowFromJson | |
| importstring | ImportString | |
| importfile | ImportFile | |
| getnextmodified | GetNextModified | |
| modify | Modify | |
| describe | Describe |
Data Expressions
Data expressions will be directly translated to the corresponding methods in the runtime library; there is no C# syntax for data expressions. Besides that, there is no implementation for setting default values for data expressions.
One item
PowerScript:
dwcontrol.Object.columnname {.buffer } {.datasource } { [ rownum ] }
C# scripts:
To get value:
TValue GetItem<TValue>(int row, string column, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary, bool isOriginalValue = false)
To set value:
void SetItem(object value, int row, string column, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary)
All items
PowerScript:
dwcontrol.Object.columnname {.buffer } {.datasource }
C# scripts:
To get value:
TValue[] GetItems<TValue>(string column, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary, bool isOriginalValue = false)
To set value:
void SetItems(object value, string column, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary)
Range of items
PowerScript:
dwcontrol.Object.columnname {.buffer } {.datasource } [ startrownum, endrownum ]
C# scripts:
To get value:
TValue[] GetItems<TValue>(string column, int startRow, int endRow, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary, bool isOriginalValue = false)
To set value:
void SetItems(object value, string column, int startRow, int endRow, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary)
Single item
PowerScript:
dwcontrol.Object.Data {.buffer } {.datasource } [ rownum, colnum ]
C# scripts:
To get value:
TValue GetItem<TValue>(int row, short column, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary, bool isOriginalValue = false)
To set value:
void SetItem(object value, int row, short column, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary)
Blocks of data
PowerScript:
dwcontrol.Object.Data {.buffer } {.datasource } [ startrownum, startcolnum, endrownum, endcolnum ]
C# scripts:
To get value:
TModel[] GetBlocks<TModel>(int startRow, short startColumn, int endRow, short endColumn, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary, bool isOriginalValue = false)
To set value:
void SetBlocks(object value, int startRow, short startColumn, int endRow, short endColumn, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary)
Single row
PowerScript:
dwcontrol.Object.Data {.buffer } {.datasource } [ rownum ]
C# scripts:
To get value:
TModel[] GetRowsData<TModel>(int startRow, int endRow, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary, bool isOriginalValue = false)
To set value:
void SetRowData(object value, int row, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary)
All rows
PowerScript:
dwcontrol.Object.Data {.buffer } {.datasource }
C# scripts:
To get value:
TModel[] GetRowsData<TModel>(DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary, bool isOriginalValue = false)
To set value:
void SetRowsData(object value, DwBuffer bufferType = DwBuffer.Primary)
Unsupported
Selected row and selected items are not supported to be translated to C#.
PowerScript for selected items:
dwcontrol.Object.columnname {.Primary }{.datasource }.Selected
PowerScript for selected rows:
dwcontrol.Object.Data {.Primary } {.datasource } .Selected
Embedded SQLs
N/A